The kinin B1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 reverses tactile and cold allodynia in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance
- PMID: 17618300
- PMCID: PMC1978253
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707388
The kinin B1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 reverses tactile and cold allodynia in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance
Abstract
Background and purpose: Diabetes causes sensory polyneuropathy with associated pain in the form of tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia which are often intractable and resistant to current therapy. This study tested the beneficial effects of the non-peptide and orally active kinin B(1) receptor antagonist SSR240612 against tactile and cold allodynia in a rat model of insulin resistance.
Experimental approach: Rats were fed with 10% D-glucose for 12 weeks and effects of orally administered SSR240612 (0.3-30 mg kg(-1)) were determined on the development of tactile and cold allodynia. Possible interference of SSR240612 with vascular oxidative stress and pancreatic function was also addressed.
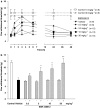
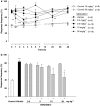
Key results: Glucose-fed rats exhibited tactile and cold allodynia, increases in systolic blood pressure and higher plasma levels of insulin and glucose, at 12 weeks. SSR240612 blocked tactile and cold allodynia at 3 h (ID(50)=5.5 and 7.1 mg kg(-1), respectively) in glucose-fed rats but had no effect in control rats. The antagonist (10 mg kg(-1)) had no effect on plasma glucose and insulin, insulin resistance (HOMA index) and aortic superoxide anion production in glucose-fed rats.
Conclusions and implications: We provide the first evidence that the B(1) receptors are involved in allodynia in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance. Allodynia was alleviated by SSR240612 most likely through a direct inhibition of B(1) receptors affecting spinal cord and/or sensory nerve excitation. Thus, orally active non-peptide B(1) receptor antagonists should have clinical therapeutic potential in the treatment of sensory polyneuropathy.
Figures
References
-
- Bélichard P, Landry M, Faye P, Bachvarov DR, Bouthillier J, Pruneau D, et al. Inflammatory hyperalgesia induced by zymosan in the plantar tissue of the rat: effect of kinin receptor antagonists. Immunopharmacology. 2000;46:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Calcutt NA, Dines KC, Ceseña RM. Effects of the peptide HP228 on nerve disorders in diabetic rats. Metabolism. 1998;47:650–656. - PubMed
-
- Calcutt NA, Freshwater JD, Mizisin AP. Prevention of sensory disorders in diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats by aldose reductase inhibition or treatment with ciliary neurotrophic factor. Diabetologia. 2004;47:718–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

