Nocistatin inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the mouse neocortex via presynaptic Gi/o protein linked pathways
- PMID: 17618307
- PMCID: PMC2050818
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707377
Nocistatin inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the mouse neocortex via presynaptic Gi/o protein linked pathways
Abstract
Background and purpose: Nocistatin (NST) is a neuropeptide generated from cleavage of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) precursor. Evidence has been presented that NST acts as a functional antagonist of N/OFQ, although NST receptor and transduction pathways have not yet been identified. We previously showed that N/OFQ inhibited [(3)H]5-hydroxytryptamine ([(3)H]5-HT) release from mouse cortical synaptosomes via activation of NOP receptors. We now investigate whether NST regulates [(3)H]5-HT release in the same preparation.
Experimental approach: Mouse and rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes in superfusion, preloaded with [(3)H]5-HT and stimulated with 1 min pulses of 10 mM KCl, were used.
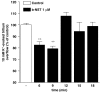
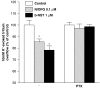
Key results: Bovine NST (b-NST) inhibited the K(+)-induced [(3)H]5-HT release, displaying similar efficacy but lower potency than N/OFQ. b-NST action underwent concentration-dependent and time-dependent desensitization, and was not prevented either by the NOP receptor antagonist [Nphe(1) Arg(14),Lys(15)]N/OFQ(1-13)-NH(2) (UFP-101) or by the non-selective opioid receptor antagonist, naloxone. Contrary to N/OFQ, b-NST reduced [(3)H]5-HT release from synaptosomes obtained from NOP receptor knockout mice. However, both N/OFQ and NST were ineffective in synaptosomes pre-treated with the G(i/o) protein inhibitor, Pertussis toxin. NST-N/OFQ interactions were also investigated. Co-application of maximal concentrations of both peptides did not result in additive effects, whereas pre-application of maximal b-NST concentrations partially attenuated N/OFQ inhibition.
Conclusions and implications: We conclude that b-NST inhibits [(3)H]5-HT release via activation of G(i/o) protein linked pathways, not involving classical opioid receptors and the NOP receptor. The present data strengthen the view that b-NST is, per se, a biologically active peptide endowed with agonist activity.
Figures
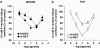
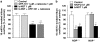
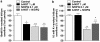
Comment in
-
Towards a receptor for nocistatin?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;152(4):415-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707384. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17618302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadi S, Kotalla C, Guhring H, Takeshima H, Pahl A, Zeilhofer HU. Modulation of synaptic transmission by nociceptin/orphanin FQ and nocistatin in the spinal cord dorsal horn of mutant mice lacking the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;59:612–618. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Matsubayashi H, Tamura Y, Takahashi T. Orphanin FQ-induced outward current in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2000;853:269–274. - PubMed
-
- Calo G, Guerrini R, Bigoni R, Rizzi A, Bianchi C, Regoli D, et al. Structure–activity study of the nociceptin(1-13)-NH2 N-terminal tetrapeptide and discovery of a nociceptin receptor antagonist. J Med Chem. 1998;41:3360–3366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

