Voiding urosonography with ultrasound contrast agents for the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux in children. I. Procedure
- PMID: 17618429
- PMCID: PMC2292498
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-007-0529-7
Voiding urosonography with ultrasound contrast agents for the diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux in children. I. Procedure
Abstract
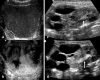
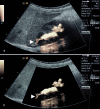
Voiding urosonography (VUS) encompasses examination of the urinary tract with intravesical administration of US contrast agent (UCA) for diagnosis of vesicoureteric reflux (VUR). The real breakthrough for US examination of VUR came with the availability of stabilized UCAs in the mid-1990s. This article presents a comprehensive review of various procedural aspects of VUS. Different US modalities are available for detecting the echogenic microbubbles: fundamental mode, colour Doppler US, harmonic imaging and dedicated contrast imaging with multiple display options. The reflux is graded (1 to 5) in a similar manner to the system used in voiding cystourethrography (VCUG). The most commonly used UCA for VUS, Levovist, is galactose-based and contains air-filled microbubbles. The recommended concentration is 300 mg/ml at a dose of 5-10%, or less than 5%, of the bladder filling volume when using fundamental or harmonic imaging modes, respectively. There are preliminary reports of VUS using a second-generation UCA, SonoVue. Here the UCA volume is less than 1% of the bladder filling volume. There is no specific contraindication to intravesical administration of UCA. The safety profile of intravesical Levovist is very high with no reports of side effects over a decade of use in VUS.
Figures





References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s004670200010', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670200010'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11793136', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11793136/'}]}
- Darge K (2002) Diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux with ultrasound. Pediatr Nephrol 17:52–60 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92123-7', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92123-7'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7915375', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7915375/'}]}
- Kaneko K, Kuwatsuru R, Fukuda Y et al (1994) Contrast sonography for detection of vesicoureteral reflux. Lancet 344:687 - PubMed
-
- None
- von Rohden L, Bosse U, Wiemann D (1995) Refluxsonographie bei Kindern mit einem Ultraschallkontrastmittel im Vergleich zur Röntgenmiktionszystourethro-graphie. Paediat Prax 49:49–58
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00247-002-0812-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-002-0812-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12447589', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12447589/'}]}
- McEwing RL, Anderson NG, Hellewell S et al (2002) Comparison of echo-enhanced ultrasound with fluoroscopic MCU for the detection of vesicoureteral reflux in neonates. Pediatr Radiol 32:853–858 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10470914', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10470914/'}]}
- Mentzel HJ, Vogt S, Patzer L et al (1999) Contrast-enhanced sonography of vesicoureterorenal reflux in children: preliminary results. AJR 173:737–740 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

