An intact median preoptic nucleus is necessary for chronic angiotensin II-induced hypertension
- PMID: 17618605
- PMCID: PMC2040032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.005
An intact median preoptic nucleus is necessary for chronic angiotensin II-induced hypertension
Abstract
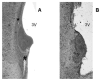
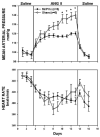
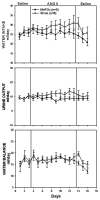
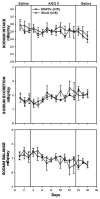
The median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) receives afferent input from the subfornical organ, a circumventricular organ that has been shown to be necessary in mediating the full chronic hypertensive response to angiotensin II (ANG II) administration. In addition, intravenous ANG II infusion has been shown to cause activation of a number of neurons in both the dorsal and ventral part of MnPO. Taken together, we hypothesized that the MnPO is necessary for the full hypertensive response observed during chronic ANG II-induced hypertension. To test this hypothesis, male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to either sham (SHAM) or electrolytic lesion of both the dorsal and ventral part of the MnPO (MnPOx). During the same surgery, rats were instrumented with venous catheters, and radiotelemetric transducers for the intravenous administration of ANG II and the measurement of blood pressure and heart rate, respectively. Rats were then given a week recovery period. After 3 days of saline control infusion, ANG II was intravenously infused (10 ngxkg(-1).min(-1)) in both sham and MnPOx animals for 10 consecutive days, and followed by 3 recovery days. By day 7 of ANG II infusion, MAP had increased 38+/-3 mm Hg in sham lesion rats (n=6), but MAP of MnPOx rats (>90% MnPO ablated; n=5) had only increased 18+/-2 mm Hg. This trend continued through day 10 of ANG II treatment. These results support the hypothesis that the MnPO is necessary for the chronic hypertensive response to ANG II administration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the median preoptic nucleus in chronic angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 31;1238:75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.020. Epub 2008 Aug 16. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18760264
-
Contribution of the subfornical organ to angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Feb;288(2):H680-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00823.2004. Epub 2004 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15458953
-
Neurons of the median preoptic nucleus contribute to chronic angiotensin II-salt induced hypertension in the rat.Physiol Rep. 2022 Dec;10(24):e15551. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15551. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36564179 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the median preoptic nucleus in the chronic hypotensive effect of losartan in sodium-replete normal rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010 Jan;37(1):e7-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05307.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19793103
-
Role of the Median Preoptic Nucleus in Arterial Pressure Regulation and Sodium and Water Homeostasis during High Dietary Salt Intake.Neurophysiology. 2012 Nov;44(5):363-375. doi: 10.1007/s11062-012-9307-8. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Neurophysiology. 2012. PMID: 32724266 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lesion of the Subfornical Organ attenuates Neuronal Activation of the Paraventricular Nucleus in response to Angiotensin II in normal rats.Open J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 23;1:1. Open J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 24795816 Free PMC article.
-
Selectively Inhibiting the Median Preoptic Nucleus Attenuates Angiotensin II and Hyperosmotic-Induced Drinking Behavior and Vasopressin Release in Adult Male Rats.eNeuro. 2019 Mar 26;6(2):ENEURO.0473-18.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0473-18.2019. eCollection 2019 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 30923740 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the median preoptic nucleus in the development of chronic deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertension.Physiol Rep. 2024 May;12(10):e16046. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16046. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38749925 Free PMC article.
-
An Essential role for DeltaFosB in the median preoptic nucleus in the sustained hypertensive effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia.Hypertension. 2012 Jul;60(1):179-87. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.193789. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22689746 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia increases blood pressure and expression of FosB/DeltaFosB in central autonomic regions.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):R131-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00830.2010. Epub 2011 May 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21543638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brody MJ, Fink GD, Buggy J, Haywood JR, Gordon FJ, Johnson AK. The role of the anteroventral third ventricle (AV3V) region in experimental hypertension. Circ Res. 1978;43:I-2–I-13.
-
- Brooks VL, Osborn JW. Hormonal-sympathetic interactions in long-term regulation of arterial pressure: An hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:R1343–58. - PubMed
-
- Cerasola G, Cottone S, D'Ignoto G, Grasso L, Carone MB, Carapelle E, Contorno A. Effects of enalapril maleate on blood pressure, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and peripheral sympathetic activity in essential hypertension. Clin Ther. 1987;9:390–399. - PubMed
-
- Ciriello J, Gutman MB. Functional identification of central pressor pathways originating in the subfornical organ. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991;69:1035–1045. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham JT, Beltz T, Johnson RF, Johnson AK. The effects of ibotenate lesions of the median preoptic nucleus on experimentally-induced and circadian drinking behavior in rats. Brain Res. 1992;580:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

