A novel cone visual cycle in the cone-dominated retina
- PMID: 17618621
- PMCID: PMC2001262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.05.003
A novel cone visual cycle in the cone-dominated retina
Abstract
The visual processing of humans is primarily reliant upon the sensitivity of cone photoreceptors to light during daylight conditions. This underscores the importance of understanding how cone photoreceptors maintain the ability to detect light. The vertebrate retina consists of a combination of both rod and cone photoreceptors. Subsequent to light exposure, both rod and cone photoreceptors are dependent upon the recycling of vitamin A to regenerate photopigments, the proteins responsible for detecting light. Metabolic processing of vitamin A in support of rod photopigment renewal, the so-called "rod visual cycle", is well established. However, the metabolic processing of vitamin A in support of cone photopigment renewal remains a challenge for characterization in the recently discovered "cone visual cycle". In this review we summarize the research that has defined the rod visual cycle and our current concept of the novel cone visual cycle. Here, we highlight the research that supports the existence of a functional cone-specific visual cycle: the identification of novel enzymatic activities that contribute to retinoid recycling, the observation of vitamin A recycling in cone-dominated retinas, and the localization of some of these activities to the Müller cell. In the opinions of the authors, additional research on the possible interactions between these two visual cycles in the duplex retina is needed to understand visual detection in the human retina.
Figures
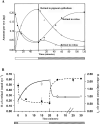
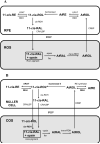
 Light adaptation,
Light adaptation,  Dark adaptation For details of experiment and results see Trevino, Villazana-Espinoza et al. 2005.
Dark adaptation For details of experiment and results see Trevino, Villazana-Espinoza et al. 2005.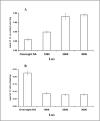
 light adaptation,
light adaptation,  dark adaptation. For details of experiments and results, see Villazana-Espinoza, Hatch et al. 2006.
dark adaptation. For details of experiments and results, see Villazana-Espinoza, Hatch et al. 2006.
 light adaptation,
light adaptation,  dark adaptation. For details of experiments and results, see Villazana-Espinoza, Hatch et al. 2006.
dark adaptation. For details of experiments and results, see Villazana-Espinoza, Hatch et al. 2006.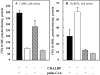
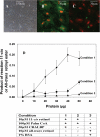
References
-
- Adler AJ, Klucznik KM. Proteins and glycoproteins of the bovine interphotoreceptor matrix: composition and fractionation. Exp Eye Res. 1982;34(3):423–34. - PubMed
-
- Blaner WS, Das SR, et al. Hydrolysis of 11-cis- and all-trans-retinyl palmitate by homogenates of human retinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(1):53–8. - PubMed
-
- Bok D. Retinal photoreceptor-pigment epithelium interactions. Friedenwald lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985;26(12):1659–94. - PubMed
-
- Bok D, Ong DE, et al. Immunocytochemical localization of cellular retinol binding protein in the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984;25(8):877–83. - PubMed
-
- Bridges CD, Alvarez RA, et al. Rhodopsin, vitamin A, and interstitial retinol-binding protein in the rd chicken. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987;28(4):613–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

