Neonatal jaundice and stool production in breast- or formula-fed term infants
- PMID: 17619902
- PMCID: PMC2668621
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-007-0533-9
Neonatal jaundice and stool production in breast- or formula-fed term infants
Abstract
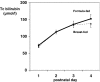
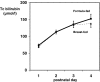
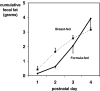
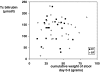
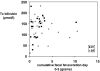
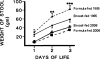
It has remained unclear whether the amount of fecal fat excreted in the stool and stool production influences the severity of neonatal jaundice. We determined the relationship between stool production, fecal fat excretion and jaundice in healthy breast-fed (BF) or formula-fed (FF) (near-)term neonates. From postnatal day 1-4, we quantitatively collected stools from 27 FF and 33 BF infants in daily fractions. Stool production and fecal fat contents were related to unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) levels, as determined by transcutaneous bilirubinometry (TcB). Bilirubin concentrations and stool production did not differ between FF and BF neonates during the study period. Neonatal bilirubin levels were not inversely correlated with stool production. FF and BF infants had similar fecal fat excretion rates. The stool production of FF infants was profoundly lower in the present study than in a 1985 study by De Carvalho et al. [J Pediatr (1985) 107:786-790]. We conclude that increased jaundice during the first postnatal days in healthy term neonates can no longer be attributed to breast-feeding and speculate that improved absorbability of formulas since 1985 has contributed to similar fat excretion and stool production in FF and BF neonates in 2007.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of diet on feces and jaundice during the first 3 weeks of life.Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):660-7. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90862-s. Gastroenterology. 1992. PMID: 1634081
-
Serum bilirubin levels in breast- and formula-fed infants in the first 5 days of life.Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Nov 15;127(10):985-9. Can Med Assoc J. 1982. PMID: 7139449 Free PMC article.
-
A controlled, randomized, double-blind trial of prophylaxis against jaundice among breastfed newborns.Pediatrics. 2005 Aug;116(2):385-91. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1807. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 16061593 Clinical Trial.
-
Importance of the regiospecific distribution of long-chain saturated fatty acids on gut comfort, fat and calcium absorption in infants.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017 Jun;121:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 Jun 4. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017. PMID: 28651696 Review.
-
Breastfeeding and human milk: their association with jaundice in the neonate.Clin Perinatol. 1987 Mar;14(1):89-107. Clin Perinatol. 1987. PMID: 3549117 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluid supplementation for neonatal unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 1;8(8):CD011891. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011891.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28762235 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, Pyruvate Kinase, and New Generation Inflammation Biomarkers in Prolonged Neonatal Jaundice.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 12;60(9):1491. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091491. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336532 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of kangaroo mother care combined with neonatal phototherapy in newborns with non-pathological jaundice: A meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Jan 25;11:1098143. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1098143. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37082708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Earlier Nutrient Fortification of Breastmilk Fed LBW Infants Improves Jaundice Related Outcomes.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 17;12(7):2116. doi: 10.3390/nu12072116. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32708857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1177/000992288502400201', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1177/000992288502400201'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '4038477', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4038477/'}]}
- Adams JA, Hey DJ, Hall RT (1985) Incidence of hyperbilirubinemia in breast- vs. formula-fed infants. Clin Pediatr 24(2):69–73 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0022-3476(05)82162-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82162-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1999786', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1999786/'}]}
- Alonso EM, Whitington PF, Whitington SH, Rivard WA, Given G (1991) Enterohepatic circulation of nonconjugated bilirubin in rats fed with human milk. J Pediatr 118(3):425–430 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1542/peds.107.3.e41', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.107.3.e41'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11230622', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11230622/'}]}
- Bertini G, Dani C, Tronchin M, Rubaltelli FF (2001) Is breastfeeding really favoring early neonatal jaundice? Pediatrics 107(3):E41 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1053/siny.2002.0100', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1053/siny.2002.0100'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12208097', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12208097/'}]}
- Bertini G, Rubaltelli FF (2002) Non-invasive bilirubinometry in neonatal jaundice. Semin Neonatol 7(2):129–133 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1542/peds.106.2.e17', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.106.2.e17'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10920173', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10920173/'}]}
- Bhutani VK, Gourley GR, Adler S, Kreamer B, Dalin C, Johnson LH (2000) Noninvasive measurement of total serum bilirubin in a multiracial predischarge newborn population to assess the risk of severe hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics 106(2):E17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

