Detection of inflammatory bowel disease: diagnostic performance of cross-sectional imaging modalities
- PMID: 17619923
- PMCID: PMC2386533
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-007-9276-3
Detection of inflammatory bowel disease: diagnostic performance of cross-sectional imaging modalities
Abstract
Different cross-sectional imaging techniques can be used as a diagnostic tool for the evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In this report the diagnostic performances of ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in the detection of IBD and the evaluation of known IBD are described, together with a short update on patient preparation and imaging technique of the respective modalities discussed.
Figures
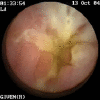





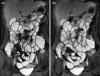
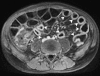
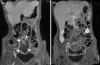
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory bowel disease: imaging of the pediatric patient.Semin Roentgenol. 2008 Jan;43(1):29-38. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2007.08.005. Semin Roentgenol. 2008. PMID: 18053826 Review. No abstract available.
-
Imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease: recent trends, questions and answers.Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2009 Jun;33 Suppl 3:S174-82. doi: 10.1016/S0399-8320(09)73152-5. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2009. PMID: 20117340
-
Imaging for Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Surg Clin North Am. 2015 Dec;95(6):1143-58, v. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Surg Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26596919 Review.
-
[Bowel imaging--a reevaluation. Part 1: Conventional techniques and ultrasonography].Rofo. 2007 Jul;179(7):683-92. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-963202. Rofo. 2007. PMID: 17592807 Review. German.
-
Imaging techniques in IBD and their role in follow-up and surveillance.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Dec;11(12):722-36. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.144. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25157623 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance colonography in severe attacks of ulcerative colitis.Eur Radiol. 2012 Sep;22(9):1963-71. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2456-8. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Eur Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22538631
-
Can diffusion weighted imaging be used as an alternative to contrast-enhanced imaging on magnetic resonance enterography for the assessment of active inflammation in Crohn disease?Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(8):e19202. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019202. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32080107 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Crohn's disease, integrated with formal consensus of experts in Japan.J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;48(1):31-72. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0673-1. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23090001 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inflammatory diseases of the bowel: diagnosis and follow-up.Pediatr Radiol. 2010 Jun;40(6):920-6. doi: 10.1007/s00247-010-1627-5. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Pediatr Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20432009 Review.
-
Contrast enhanced ultrasound: comparing a novel modality to MRI to assess for bowel disease in pediatric Crohn's patients.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Apr 5;5:13. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2019.11.02. eCollection 2020. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32258517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1053/j.gastro.2004.01.063', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2004.01.063'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15168363', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15168363/'}]}
- Loftus EV Jr (2004) Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 126:1504–1517 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11218235', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11218235/'}]}
- Farrokhyar F, Swarbrick ET, Irvine EJ (2001) A critical review of epidemiological studies in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 36:2–15 - PubMed
-
- None
- Stenson WF (2004) Inflammatory bowel disease, Chap. 142 (on-line edition). In: Goldman L, Aussiello D, (eds). Cecil textbook of medicine, 22nd edn. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunder
-
- None
- Friedman S, Blumberg RS (2005) Inflammatory bowel disease, Chap. 172 (on-line edition). In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, (eds). Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 16th edn. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/gut.2005.081950a', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.081950a'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1859998', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1859998/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16481628', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16481628/'}]}
- Stange EF, Travis SP, Vermeire S, et al. (2006) European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: definitions and diagnosis. Gut 55(Suppl 1):i1–i15 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

