A novel horse alpha-defensin: gene transcription, recombinant expression and characterization of the structure and function
- PMID: 17620056
- PMCID: PMC2049026
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070747
A novel horse alpha-defensin: gene transcription, recombinant expression and characterization of the structure and function
Abstract
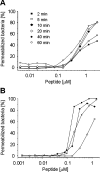
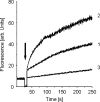
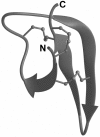
Defensins are a predominant class of antimicrobial peptides, which act as endogenous antibiotics. Defensins are classified into three distinct sub-families: theta-, beta-, and alpha-defensins. Synthesis of alpha-defensin has been confirmed only in primates and glires to date and is presumably unique for a few tissues, including neutrophils and Paneth cells of the small intestine. Antimicrobial activities of these peptides were shown against a wide variety of microbes including bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan parasites. In the present study, we report the characterization of the equine alpha-defensin DEFA (defensin alpha) 1. Transcription analysis revealed that the transcript of the gene is present in the small intestine only. An alignment with known alpha-defensins from primates and glires displayed a homology with Paneth-cell-specific alpha-defensins. DEFA1 was recombinantly expressed in Escherichia coli and subsequently analysed structurally by CD and molecular modelling. To examine the antimicrobial properties, a radial diffusion assay was performed with 12 different micro-organisms and the LD90 (lethal dose killing > or =90% of target organism) and MBC (minimal bactericidal concentration) values were examined. DEFA1 showed an antimicrobial activity against different Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and against the yeast Candida albicans. Using viable bacteria in combination with a membrane-impermeable fluorescent dye, as well as depolarization of liposomes as a minimalistic system, it became evident that membrane permeabilization is at least an essential part of the peptide's mode of action.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The repertoire of equine intestinal alpha-defensins.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 23;10:631. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-631. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20030839 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial properties of the equine alpha-defensin DEFA1 against bacterial horse pathogens.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009 Jul 15;130(1-2):102-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.01.005. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19211153
-
Solution structure and functional studies of the highly potent equine antimicrobial peptide DEFA1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Apr 17;459(4):668-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.168. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25769951
-
Events at the host-microbial interface of the gastrointestinal tract. V. Paneth cell alpha-defensins in intestinal host defense.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):G173-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00079.2005. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16014978 Review.
-
Expression and regulation of antimicrobial peptides in the gastrointestinal tract.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Jan;75(1):49-58. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0503249. Epub 2003 Oct 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 14525966 Review.
Cited by
-
Paneth cells in farm animals: current status and future direction.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 15;14(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00905-5. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37582766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An evaluation of fusion partner proteins for paratransgenesis in Asaia bogorensis.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 1;17(9):e0273568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273568. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36048823 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro potential of equine DEFA1 and eCATH1 as alternative antimicrobial drugs in rhodococcosis treatment.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Apr;56(4):1749-55. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05797-11. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22232283 Free PMC article.
-
The repertoire of equine intestinal alpha-defensins.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 23;10:631. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-631. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20030839 Free PMC article.
-
AhR Activation Transcriptionally Induces Anti-Microbial Peptide Alpha-Defensin 1 Leading to Reversal of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Colitis.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2460538. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2460538. Epub 2025 Feb 2. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39894796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: basic facts and emerging concepts. J. Intern. Med. 2003;254:197–215. - PubMed
-
- Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 2002;415:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Ganz T. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;40:710–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

