Implication of quorum sensing in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence: the luxS gene is necessary for expression of genes in pathogenicity island 1
- PMID: 17620352
- PMCID: PMC2044537
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01942-06
Implication of quorum sensing in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence: the luxS gene is necessary for expression of genes in pathogenicity island 1
Abstract
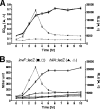
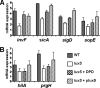
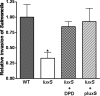
Despite the fact that the regulatory system sensing density of cell population and its signaling molecule have been identified in Salmonella enterica, the biological significance of this phenomenon termed as quorum sensing remains unknown. In this report, we provide evidence that the luxS gene is necessary for Salmonella virulence phenotypes. Transcription assays showed that the cell-density-dependent induction of the invF gene was abolished in a Salmonella strain with the luxS gene deleted. The effect of the luxS deletion was also investigated in other InvF-regulated genes expressed from Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1). The decreased expression of SPI-1 genes in the strain with luxS deleted could be restored by either the addition of a synthetic signal molecule or the introduction of a plasmid copy of the luxS gene. Thus, the reduced expression of invF and its regulated genes in Salmonella cells lacking quorum sensing resulted in the attenuation of virulence phenotypes both in vitro and in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Bajaj, V., C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1995. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol. Microbiol. 18:715-727. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Burgess, N. A., D. F. Kirke, P. Williams, K. Winzer, K. R. Hardie, N. L. Meyers, J. Aduse-Opoku, M. A. Curtis, and M. Camara. 2002. LuxS-dependent quorum sensing in Porphyromonas gingivalis modulates protease and haemagglutinin activities but is not essential for virulence. Microbiology 148:763-772. - PubMed
-
- Chan, R. K., D. Botstein, T. Watanabe, and Y. Ogata. 1972. Specialized transduction of tetracycline resistance by phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. II. Properties of a high-frequency-transducing lysate. Virology 50:883-898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

