A functionally specialized population of mucosal CD103+ DCs induces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta and retinoic acid-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 17620361
- PMCID: PMC2118683
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070590
A functionally specialized population of mucosal CD103+ DCs induces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta and retinoic acid-dependent mechanism
Abstract
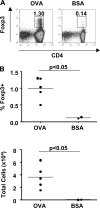
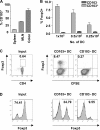
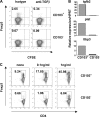
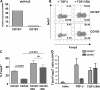
Foxp3(+) regulatory T (T reg) cells play a key role in controlling immune pathological re actions. Many develop their regulatory activity in the thymus, but there is also evidence for development of Foxp3(+) T reg cells from naive precursors in the periphery. Recent studies have shown that transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta can promote T reg cell development in culture, but little is known about the cellular and molecular mechanisms that mediate this pathway under more physiological conditions. Here, we show that after antigen activation in the intestine, naive T cells acquire expression of Foxp3. Moreover, we identify a population of CD103(+) mesenteric lymph node dendritic cells (DCs) that induce the development of Foxp3(+) T reg cells. Importantly, promotion of T reg cell responses by CD103(+) DCs is dependent on TGF-beta and the dietary metabolite, retinoic acid (RA). These results newly identify RA as a cofactor in T reg cell generation, providing a mechanism via which functionally specialized gut-associated lymphoid tissue DCs can extend the repertoire of T reg cells focused on the intestine.
Figures
Comment in
-
Oral tolerance: is it all retinoic acid?J Exp Med. 2007 Aug 6;204(8):1737-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071251. Epub 2007 Jul 9. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17620364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coombes, J.L., N.J. Robinson, K.J. Maloy, H.H. Uhlig, and F. Powrie. 2005. Regulatory T cells and intestinal homeostasis. Immunol. Rev. 204:184–194. - PubMed
-
- Kretschmer, K., I. Apostolou, D. Hawiger, K. Khazaie, M.C. Nussenzweig, and H. von Boehmer. 2005. Inducing and expanding regulatory T cell populations by foreign antigen. Nat. Immunol. 6:1219–1227. - PubMed
-
- Sun, J.B., S. Raghavan, A. Sjoling, S. Lundin, and J. Holmgren. 2006. Oral tolerance induction with antigen conjugated to cholera toxin B subunit generates both Foxp3+CD25+ and Foxp3−CD25− CD4+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 177:7634–7644. - PubMed
-
- Thorstenson, K.M., and A. Khoruts. 2001. Generation of anergic CD25+CD4+ T cells with immunoregulatory potential in vivo following induction of peripheral tolerance with intravenous or oral antigen. J. Immunol. 167:188–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

