Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 T reg cells via retinoic acid
- PMID: 17620362
- PMCID: PMC2118682
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20070602
Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 T reg cells via retinoic acid
Abstract
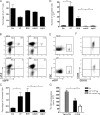
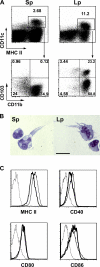
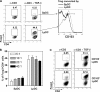
To maintain immune homeostasis, the intestinal immune system has evolved redundant regulatory strategies. In this regard, the gut is home to a large number of regulatory T (T reg) cells, including the Foxp3(+) T reg cell. Therefore, we hypothesized that the gut environment preferentially supports extrathymic T reg cell development. We show that peripheral conversion of CD4(+) T cells to T reg cells occurs primarily in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) after oral exposure to antigen and in a lymphopenic environment. Dendritic cells (DCs) purified from the lamina propria (Lp; LpDCs) of the small intestine were found to promote a high level of T reg cell conversion relative to lymphoid organ-derived DCs. This enhanced conversion by LpDCs was dependent on TGF-beta and retinoic acid (RA), which is a vitamin A metabolite highly expressed in GALT. Together, these data demonstrate that the intestinal immune system has evolved a self-contained strategy to promote T reg cell neoconversion.
Figures



Comment in
-
Oral tolerance: is it all retinoic acid?J Exp Med. 2007 Aug 6;204(8):1737-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071251. Epub 2007 Jul 9. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17620364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jordan, M.S., A. Boesteanu, A.J. Reed, A.L. Petrone, A.E. Holenbeck, M.A. Lerman, A. Naji, and A.J. Caton. 2001. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat. Immunol. 2:301–306. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli, E., Y. Carrier, W. Gao, T. Korn, T.B. Strom, M. Oukka, H.L. Weiner, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2006. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

