Mice deficient for the type II transmembrane serine protease, TMPRSS1/hepsin, exhibit profound hearing loss
- PMID: 17620368
- PMCID: PMC1934525
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070068
Mice deficient for the type II transmembrane serine protease, TMPRSS1/hepsin, exhibit profound hearing loss
Abstract
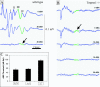
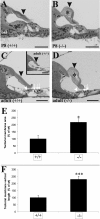
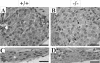
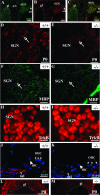
Defective proteolysis has been implicated in hearing loss through the discovery of mutations causing autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a type II transmembrane serine protease gene, TMPRSS3. To investigate their physiological function and the contribution of this family of proteases to the auditory function, we analyzed the hearing status of mice deficient for hepsin, also known as TMPRSS1. These mice exhibited profound hearing loss with elevated hearing thresholds compared with their heterozygous and wild-type littermates. Their cochleae showed abnormal tectorial membrane development, reduction in fiber compaction in the peripheral portion of the auditory nerve, and decreased expression of the myelin proteins myelin basic protein and myelin protein zero. In addition, reduced level of the large conductance voltage- and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel was detected in the sensory hair cells of Tmprss1-null mice. We examined thyroid hormone levels in Tmprss1-deficient mice, as similar cochlear defects have been reported in animal models of hypothyroidism, and found significantly reduced free thyroxine levels. These data show that TMPRSS1 is required for normal auditory function. Hearing impairment present in Tmprss1-null mice is characterized by a combination of various structural, cellular, and molecular abnormalities that are likely to affect different cochlear processes.
Figures
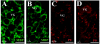
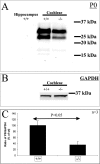
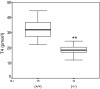
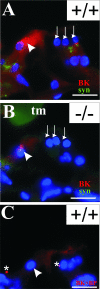
References
-
- Morton NE. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1991;630:16–31. - PubMed
-
- Seidman MD, Ahmad N, Bai U. Molecular mechanisms of age-related hearing loss. Ageing Res Rev. 2002;1:331–343. - PubMed
-
- Gratton MA, Vazquez AE. Age-related hearing loss: current research. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11:367–371. - PubMed
-
- Scott HS, Kudoh J, Wattenhofer M, Shibuya K, Berry A, Chrast R, Guipponi M, Wang J, Kawasaki K, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Younus F, Mehdi SQ, Radhakrishna U, Papasavvas MP, Gehrig C, Rossier C, Korostishevsky M, Gal A, Shimizu N, Bonne-Tamir B, Antonarakis SE. Insertion of beta-satellite repeats identifies a transmembrane protease causing both congenital and childhood onset autosomal recessive deafness. Nat Genet. 2001;27:59–63. - PubMed
-
- Masmoudi S, Antonarakis SE, Schwede T, Ghorbel AM, Gratri M, Pappasavas MP, Drira M, Elgaied-Boulila A, Wattenhofer M, Rossier C, Scott HS, Ayadi H, Guipponi M. Novel missense mutations of TMPRSS3 in two consanguineous Tunisian families with non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness. Hum Mutat. 2001;18:101–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

