Renal damage in obstructive nephropathy is decreased in Skp2-deficient mice
- PMID: 17620370
- PMCID: PMC1934544
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070279
Renal damage in obstructive nephropathy is decreased in Skp2-deficient mice
Abstract
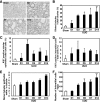
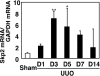
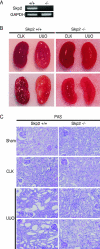
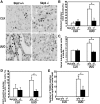
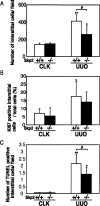
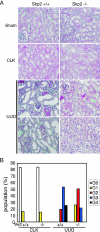
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 mediated by SCF-Skp2 ubiquitin ligase is involved in cell cycle regulation. Proliferation of tubular cells is a characteristic feature in obstructed kidneys of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Comparing Skp2(+/+) mice with Skp2(-/-) mice, we investigated the involvement of Skp2, a component of SCF-Skp2 ubiquitin ligase for p27, in the progression of renal lesions in unilateral ureteral obstructed kidneys. mRNA expression of Skp2 was markedly increased in the obstructed kidneys from Skp2(+/+) mice and peaked 3 days after unilateral ureteral obstruction. Renal atrophy, tubular dilatation, tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and increases in alpha-smooth muscle actin expression, the number of tubular cells, and proliferating tubular cells positive for Ki67 were observed in the obstructed kidneys from Skp2(+/+) mice; however, these findings were significantly attenuated in Skp2(-/-) mice. The p27 protein level was increased in the obstructed kidneys but was significantly greater in Skp2(-/-) mice. The number of Ki67-positive p27-negative cells was lower in obstructed kidneys from Skp2(-/-) mice than Skp2(+/+) mice, whereas that of Ki67-negative p27-positive cells was greater in Skp2(-/-) mice. These findings suggest that p27 accumulation, which results from SCF-Skp2 ubiquitin ligase deficiency in Skp2(-/-) mice, is involved in the amelioration of renal damage induced by obstructive nephropathy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The amelioration of renal damage in Skp2-deficient mice canceled by p27 Kip1 deficiency in Skp2-/- p27-/- mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036249. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558406 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of Cks1 and Skp2 with TNFα/NF-κB signaling in chronic progressive nephropathy.Genes Cells. 2011 Nov;16(11):1110-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01553.x. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 22017545
-
Roles of the Skp2/p27 axis in the progression of chronic nephropathy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Sep;70(18):3277-87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1232-x. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23255047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase.Nature. 2004 Mar 11;428(6979):190-3. doi: 10.1038/nature02330. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15014502
-
Control of DNA synthesis and mitosis by the Skp2-p27-Cdk1/2 axis.Mol Cell. 2004 May 21;14(4):414-6. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00268-0. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15149588 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanoregulation of proliferation.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;29(18):5104-14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00465-09. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19596792 Free PMC article.
-
CBGA ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis in nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 18;13(1):6341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33507-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37072467 Free PMC article.
-
The amelioration of renal damage in Skp2-deficient mice canceled by p27 Kip1 deficiency in Skp2-/- p27-/- mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036249. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558406 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in kidney diseases.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012 Aug;16(4):507-17. doi: 10.1007/s10157-012-0643-1. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22684356 Review.
-
Decrease in tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor-associated death domain results from ubiquitin-dependent degradation in obstructive renal injury in rats.Am J Pathol. 2009 Jul;175(1):74-83. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080884. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19541932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walton G, Buttyan R, Garcia ME, Olsson CA, Hensle TW, Sawczuk IS. Renal growth factor expression during the early phase of experimental hydronephrosis. J Urol. 1992;148:510–514. - PubMed
-
- Klahr S, Morrissey J. Obstructive nephropathy and renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol. 2002;283:F861–F875. - PubMed
-
- Couser WG, Johnson RJ. Mechanisms of progressive renal disease in glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;23:193–198. - PubMed
-
- Gobe GC, Axelsen RA. Genesis of renal tubular atrophy in experimental hydronephrosis in the rat: role of apoptosis. Lab Invest. 1987;56:273–281. - PubMed
-
- Morgan DO. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995;374:131–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

