Chromatin disassembly from the PHO5 promoter is essential for the recruitment of the general transcription machinery and coactivators
- PMID: 17620413
- PMCID: PMC2099613
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00981-07
Chromatin disassembly from the PHO5 promoter is essential for the recruitment of the general transcription machinery and coactivators
Abstract
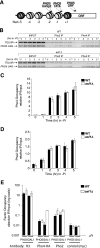
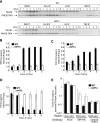
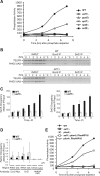
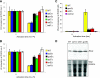
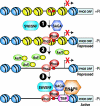
The disassembly of promoter nucleosomes appears to be a general property of highly transcribed eukaryotic genes. We have previously shown that the disassembly of chromatin from the promoters of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 and PHO8 genes, mediated by the histone chaperone anti-silencing function 1 (Asf1), is essential for transcriptional activation upon phosphate depletion. This mechanism of transcriptional regulation is shared with the ADY2 and ADH2 genes upon glucose removal. Promoter chromatin disassembly by Asf1 is required for recruitment of TBP and RNA polymerase II, but not the Pho4 and Pho2 activators. Furthermore, accumulation of SWI/SNF and SAGA at the PHO5 promoter requires promoter chromatin disassembly. By contrast, the requirement for SWI/SNF and SAGA to facilitate Pho4 activator recruitment to the nucleosome-buried binding site in the PHO5 promoter occurs prior to chromatin disassembly and is distinct from the stable recruitment of SWI/SNF and SAGA that occurs after chromatin disassembly.
Figures
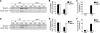
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional activators are dispensable for transcription in the absence of Spt6-mediated chromatin reassembly of promoter regions.Mol Cell. 2006 Feb 3;21(3):405-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.12.010. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16455495
-
Promoter occupancy is a major determinant of chromatin remodeling enzyme requirements.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(7):2698-707. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2698-2707.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15767675 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of the NuA4 complex poises the PHO5 promoter for chromatin remodeling and activation.EMBO J. 2004 Jul 7;23(13):2597-607. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600230. Epub 2004 Jun 3. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15175650 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast PHO5 promoter: from single locus to systems biology of a paradigm for gene regulation through chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(17):10888-902. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku784. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25190457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factors vs nucleosomes: regulation of the PHO5 promoter in yeast.Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Mar;22(3):93-7. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01001-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997. PMID: 9066259 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H3 lysine 4 hypermethylation prevents aberrant nucleosome remodeling at the PHO5 promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(15):3171-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05017-11. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21646424 Free PMC article.
-
SWI/SNF and RSC cooperate to reposition and evict promoter nucleosomes at highly expressed genes in yeast.Genes Dev. 2018 May 1;32(9-10):695-710. doi: 10.1101/gad.312850.118. Epub 2018 May 21. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29785963 Free PMC article.
-
Unwinding and rewinding the nucleosome inner turn: force dependence of the kinetic rate constants.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2013 Jan;87(1):012710. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.012710. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2013. PMID: 23410362 Free PMC article.
-
FACT and the proteasome promote promoter chromatin disassembly and transcriptional initiation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23461-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.019562. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19574230 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mapping of yeast histone chaperone anti-silencing function 1 reveals its role in condensin binding with chromatin.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 29;9(9):e108652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108652. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25264624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, A. G., D. E. Kaiser, and C. A. T. Stearns. 1997. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Adkins, M. W., S. R. Howar, and J. K. Tyler. 2004. Chromatin disassembly mediated by the histone chaperone Asf1 is essential for transcriptional activation of the yeast PHO5 and PHO8 genes. Mol. Cell 14:657-666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
