The new neurobiology of autism: cortex, connectivity, and neuronal organization
- PMID: 17620483
- PMCID: PMC2597785
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.64.7.945
The new neurobiology of autism: cortex, connectivity, and neuronal organization
Erratum in
- Arch Neurol. 2007 Oct;64(10):1464
Abstract
This review covers a fraction of the new research developments in autism but establishes the basic elements of the new neurobiologic understanding of autism. Autism is a polygenetic developmental neurobiologic disorder with multiorgan system involvement, though it predominantly involves central nervous system dysfunction. The evidence supports autism as a disorder of the association cortex, both its neurons and their projections. In particular, it is a disorder of connectivity, which appears, from current evidence, to primarily involve intrahemispheric connectivity. The focus of connectivity studies thus far has been on white matter, but alterations in functional magnetic resonance imaging activation suggest that intracortical connectivity is also likely to be disturbed. Furthermore, the disorder has a broad impact on cognitive and neurologic functioning. Deficits in high-functioning individuals occur in processing that places high demands on integration of information and coordination of multiple neural systems. Intact or enhanced abilities share a dependence on low information-processing demands and local neural connections. This multidomain model with shared characteristics predicts an underlying pathophysiologic mechanism that impacts the brain broadly, according to a common neurobiologic principle. The multiorgan system involvement and diversity of central nervous system findings suggest an epigenetic mechanism.
Figures
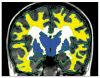

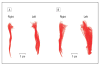
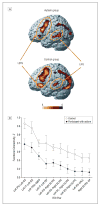
Comment in
-
No new neurobiology yet for autism.Arch Neurol. 2008 Jan;65(1):155; author reply 155-6. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2007.25. Arch Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18195158 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Baird G, Simoff E, Pickles A, et al. Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in south Thames: the special needs and autism project (SNAP) Lancet. 2006;368(9531):210–215. - PubMed
-
- Minshew NJ, Meyer J, Goldstein G. Abstract reasoning in autism: a dissociation between concept formation and concept identification. Neuropsychology. 2002;16(3):327–334. - PubMed
-
- Folstein S. Twin and adoption studies in child and adolescent psychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1996;8(4):339–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

