GPIHBP1: an endothelial cell molecule important for the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons
- PMID: 17620854
- PMCID: PMC2888298
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3281527914
GPIHBP1: an endothelial cell molecule important for the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons
Abstract
Purpose of review: To summarize recent data indicating that glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1) plays a key role in the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons.
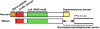
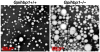
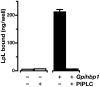
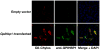
Recent findings: Lipoprotein lipase hydrolyses triglycerides in chylomicrons at the luminal surface of the capillaries in heart, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. The endothelial cell molecule that facilitates the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons has never been clearly defined. Mice lacking GPIHBP1 manifest chylomicronemia, with plasma triglyceride levels as high as 5000 mg/dl. In wild-type mice, GPIHBP1 is expressed on the luminal surface of capillaries in heart, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. Cells transfected with GPIHBP1 bind both chylomicrons and lipoprotein lipase avidly.
Summary: The chylomicronemia in Gpihbp1-deficient mice, the fact that GPIHBP1 is located within the lumen of capillaries, and the fact that GPIHBP1 binds lipoprotein lipase and chylomicrons suggest that GPIHBP1 is a key platform for the lipolytic processing of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
Figures



References
-
- Havel RJ, Kane JP. Introduction: Structure and metabolism of plasma lipoproteins. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, et al., editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 2705–2716.
-
- Bengtsson G, Olivecrona T. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein CII. Demonstration of an effect of the activator on the binding of the enzyme to milk-fat globules. FEBS Lett. 1982;147:183–187. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson G, Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase: some effects of activator proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1980;106:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson G, Olivecrona T. Apolipoprotein CII enhances hydrolysis of monoglycerides by lipoprotein lipase, but the effect is abolished by fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1979;106:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Kane JP, Havel RJ. Disorders of the biogenesis and secretion of lipoproteins containing the B apolipoproteins. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, et al., editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 2717–2752.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

