High expression of RelA/p65 is associated with activation of nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent signaling in pancreatic cancer and marks a patient population with poor prognosis
- PMID: 17622249
- PMCID: PMC2360349
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603878
High expression of RelA/p65 is associated with activation of nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent signaling in pancreatic cancer and marks a patient population with poor prognosis
Abstract
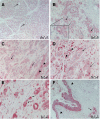
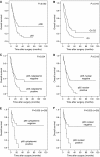
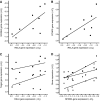
Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling was observed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines and tumours. However, information on the expression of RelA/p65, the major transcription activating NF-kappaB subunit, in these carcinomas and possible correlations thereof with NF-kappaB activation and patient survival is not available. To provide this missing translational link, we analysed expression of RelA/p65 in 82 pancreatic adenocarcinomas by immunohistochemistry. Moreover, we measured activation of the NF-kappaB pathway in 11 tumours by quantitative PCR for NF-kappaB target genes. We observed strong cytoplasmic or nuclear expression of RelA/p65 in 42 and 37 carcinomas, respectively. High cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of RelA/p65 had negative prognostic impact with 2-year survival rates for patients without cytoplasmic or nuclear RelA/p65 positivity of 41 and 40% and rates for patients with strong cytoplasmic or nuclear RelA/p65 expression of 22 and 20%, respectively. High RelA/p65 expression was correlated to increased expression of NF-kappaB target genes. The observation that high expression of RelA/p65 is correlated to an activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and indicates poor patient survival identifies a patient subgroup that might particularly benefit from NF-kappaB-inhibiting agents in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Based on our findings, this subgroup could be identified by applying simple immunohistochemical techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Jan;5(1):119-27. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 9918209
-
[Expression of heparanase and nuclear factor kappa B in pancreatic adenocarcinoma].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Aug;27(8):1267-70. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17715045 Chinese.
-
Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to hedgehog signaling pathway activation through sonic hedgehog induction in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 15;66(14):7041-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4588. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16849549
-
Reprogramming RelA.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):869-72. Epub 2004 Jul 4. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15190199 Review.
-
Negative regulation of RelA phosphorylation: emerging players and their roles in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Feb;26(1):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 25438737 Review.
Cited by
-
HDAC inhibitors, MS-275 and salermide, potentiates the anticancer effect of EF24 in human pancreatic cancer cells.EXCLI J. 2016 Apr 4;15:246-55. doi: 10.17179/excli2016-186. eCollection 2016. EXCLI J. 2016. PMID: 27330528 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Physiopathologic and Pharmacologic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 18;14(10):2486. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102486. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic pathways in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2008 Jul 24;7:64. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-64. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18652674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
W346 inhibits cell growth, invasion, induces cycle arrest and potentiates apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells in vitro through the NF-κB signaling pathway.Tumour Biol. 2016 Apr;37(4):4791-801. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4277-2. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26520440
-
Nuclear factor κB activity correlates with the progression and prognosis of pancreatic cancer in a mouse model.Surg Today. 2013 Feb;43(2):171-7. doi: 10.1007/s00595-012-0279-5. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Surg Today. 2013. PMID: 22892758
References
-
- Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear factor-κB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell 6: 203–208 - PubMed
-
- Algül H, Adler G, Schmid RM (2002) NF-κB/Rel transcriptional pathway: implications in pancreatic cancer. Int J Gastrointest Cancer 31: 71–78 - PubMed
-
- Arlt A, Gehrz A, Müerköster S, Vorndamm J, Kruse M-L, Fölsch UR, Schäfer H (2003) Role of NF-κB and Akt/PI3K in the resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines against gemcitabine-induced cell death. Oncogene 22: 3243–3251 - PubMed
-
- Arlt A, Vorndamm J, Breitenbroich M, Fölsch UR, Kalthoff H, Schmidt WE, Schäfer H (2001) Inhibition of NF-κB sensitizes human pancreatic carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by etoposide (VP16) or doxorubicin. Oncogene 20: 859–868 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

