Potential of diallyl sulfide bearing pH-sensitive liposomes in chemoprevention against DMBA-induced skin papilloma
- PMID: 17622315
- PMCID: PMC1952677
- DOI: 10.2119/2006–00111.Khan
Potential of diallyl sulfide bearing pH-sensitive liposomes in chemoprevention against DMBA-induced skin papilloma
Abstract
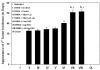
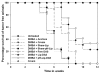
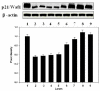
Diallyl sulfide (DAS), an active component of garlic, possesses strong anti-neoplastic properties against various forms of cancer. In the present study, we have evaluated chemo-preventive effects of liposomized DAS (conventional egg PC and pH-sensitive liposomes) against DMBA-induced skin papilloma. Various liposome-based novel formulations of DAS (250 microg/mouse) were applied topically, after one hour of exposure to DMBA (52 microg/mouse/dose), to the animals. The animals were treated thrice weekly for the total period of 12 weeks. The efficacy of the various liposomal formulations of DAS was evaluated on the basis of parameters such as incidence of tumorogenesis and total numbers and sizes of induced tumor nodules. The liposomized DAS formulations also were assessed for their effect on the expression of p53wt, p53mut, and p21/Waf1. The results of the present study showed that liposomized DAS could effectively delay the onset of tumorogenesis and reduce the cumulative numbers and sizes of tumor papillomas in treated mice. Treatment of DMBA-exposed animals with the liposomal formulation of DAS ensued in upregulation of p53wt and p21/Waf1, while levels of p53mut expression reduced down. The promising chemo-preventive nature of liposomal DAS may form the basis for establishing effective means of controlling various forms of cancer, including skin papilloma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of p53 in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced skin tumors by diallyl sulfide in Swiss albino mice.Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Nov;3(11):1459-66. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. PMID: 15542785
-
Regulation of p21/ras protein expression by diallyl sulfide in DMBA induced neoplastic changes in mouse skin.Cancer Lett. 2006 Oct 8;242(1):28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.10.049. Epub 2006 Jan 30. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 16448747
-
Involvement of multiple signaling pathways in diallyl sulfide mediated apoptosis in mouse skin tumors.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006 Oct-Dec;7(4):556-62. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006. PMID: 17250426
-
Mechanisms of inhibition of chemical toxicity and carcinogenesis by diallyl sulfide (DAS) and related compounds from garlic.J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):1041S-5S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.1041S. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11238812 Review.
-
Antioxidants in chemoprevention of skin cancer.Curr Probl Dermatol. 2001;29:128-39. doi: 10.1159/000060662. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11225193 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Liposomal Diallyl Disulfide and Oxaliplatin on Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 20;14(2):236. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020236. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35213970 Free PMC article.
-
New Enlightenment of Skin Cancer Chemoprevention through Phytochemicals: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and the Underlying Mechanisms.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:243452. doi: 10.1155/2014/243452. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24757666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Formulation of Diallyl Trisulfide Chemosensitizes the Growth Inhibitory Activity of Doxorubicin in Colorectal Cancer Model: A Novel In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Analysis.Molecules. 2022 Mar 28;27(7):2192. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072192. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408590 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-mediated synthesis of 5-FU based nanoparticles employing orange fruit juice: a novel drug delivery system to treat skin fibrosarcoma in model animals.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 23;9(1):12288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48180-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31444363 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-Based Nanoformulations of [6]-Gingerol for the Chemoprevention of Benzo[a] Pyrene-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis: Preclinical Evidence.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;18(4):574. doi: 10.3390/ph18040574. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Block E. The chemistry of garlic and onions. Sci Am. 1985;252:114–9. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal KC. Therapeutic actions of garlic constituents. Med Res Rev. 1996;16:111–24. - PubMed
-
- Arora A, Kalra N, Shukla Y. Regulation of p21/ras protein expression by diallyl sulfide in DMBA induced neoplastic changes in mouse skin. Cancer Lett. 2006;242:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Prasad S, Kalra N, Shukla Y. Modulatory effects of diallyl sulfide against testosterone-induced oxidative stress in Swiss albino mice. Asian J Androl. 2006;8:719–23. - PubMed
-
- Haber-Mignard D, Suschetet M, Berges R, Astorg P, Siess MH. Inhibition of aflatoxin B1 and N-nitrosodiethylamine induced liver pre-neoplastic foci in rats fed naturally occurring allyl sulfides. Nutr Cancer. 1996;25:61–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
