The effects of scripted peer tutoring and programming common stimuli on social interactions of a student with autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 17624077
- PMCID: PMC1885403
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2007.160-05
The effects of scripted peer tutoring and programming common stimuli on social interactions of a student with autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
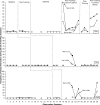
This study examined the effects of scripted peer-tutoring reading activities, with and without programmed common play-related stimuli, on social interactions between a kindergartner with autism spectrum disorder and his typically developing peer-tutoring partners during free play. A withdrawal design with multiple baselines across peers showed no effects of peer tutoring on social interactions. A withdrawal design with 1 peer and continuing baselines across the other 2 peers showed that adding play-related common stimuli to the peer-tutoring activity increased social interactions during free play.
Figures
References
-
- Esbenshade P.H, Rosales-Ruiz J. Programming common stimuli to promote generalized question-asking: A case demonstration in a child with autism. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions. 2001;3:199–210.
-
- Fuchs D, Fuchs L, Thompson A, Al Otaiba S, Yen L, McMaster K, et al. Peer-assisted learning strategies: Kindergarten reading teacher manual. 2001.
-
- Fuchs D, Fuchs L.S, Thompson A, Al Otaiba S, Yen L, Yang N.J, et al. Is reading important in reading-readiness programs? A randomized field trial with teachers as program implementers. Journal of Educational Psychology. 2001;93:251–267.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical