Androgen administration to aged male mice increases anti-anxiety behavior and enhances cognitive performance
- PMID: 17625503
- PMCID: PMC2572829
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301498
Androgen administration to aged male mice increases anti-anxiety behavior and enhances cognitive performance
Abstract
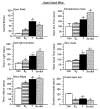
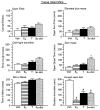
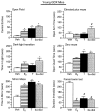
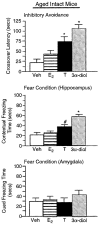
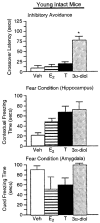
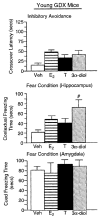
Although androgen secretion is reduced with aging, and may underlie decrements in cognitive and affective performance, the effects and mechanisms of androgens to mediate these behaviors are not well understood. Testosterone (T), the primary male androgen, is aromatized to estrogen (E(2)), and reduced to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is converted to 5alpha-androstane, 3alpha, 17beta-diol (3alpha-diol). To ascertain whether actions of the neuroactive metabolite of T, 3alpha-diol, mediates cognitive and affective behaviors, intact, aged male C57/B6 mice (24 month old) as well as young, intact and gonadectomized (GDX; 12 week old) mice were administered s.c. T, 3alpha-diol, E(2), or sesame oil vehicle (1 mg/kg; n=4-5/group) at weekly intervals and 1 h later mice were tested in the activity box, roto-rod, open field, elevated plus maze, zero maze, mirror maze, dark-light transition, forced swim, or Vogel tasks. Mice were trained in the inhibitory avoidance or conditioned contextual fear and were administered hormones following training and then were tested. After the last test occasion, tissues were collected for evaluation of hormone levels and effects on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-stimulated chloride flux. T, 3alpha-diol, or E(2) increased anti-anxiety and antidepressant behavior of aged, intact mice in the open field, light-dark transition, mirror maze, and forced swim tasks. T or 3alpha-diol, but not E(2), enhanced anti-anxiety behavior in the elevated plus maze, zero maze, and the Vogel task, and increased motor behavior in the activity monitor, latency to fall in the Roto-rod task, and cognitive performance in the hippocampally-mediated, but not the amygdala-mediated, portion of the conditioned fear task and in the inhibitory avoidance task. Anti-anxiety and enhanced cognitive performance was associated with regimen that increased plasma and hippocampal 3alpha-diol levels and GABA-stimulated chloride flux. Similar patterns were seen among young, adult GDX but not in intact mice. Thus, 3alpha-diol can enhance affective and cognitive behavior of male mice.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors neither have any conflict of interest relating to the subject of this report nor do they have financial holdings (stocks, bonds or donations of supplies or equipment) that a reasonable person would construe as possibly influencing the objectivity of the report. Professor Frye has received compensation as a consultant for The Biocontinuum Group. She has received grant support from NSF, NIMH, NIDA, NIAA, The Department of Defense and The Epilepsy Foundation of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgens with activity at estrogen receptor beta have anxiolytic and cognitive-enhancing effects in male rats and mice.Horm Behav. 2008 Nov;54(5):726-34. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.07.013. Epub 2008 Aug 8. Horm Behav. 2008. PMID: 18775724 Free PMC article.
-
3alpha-androstanediol, but not testosterone, attenuates age-related decrements in cognitive, anxiety, and depressive behavior of male rats.Front Aging Neurosci. 2010 Apr 8;2:15. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00015. eCollection 2010. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20552051 Free PMC article.
-
Mnemonic effects of testosterone and its 5alpha-reduced metabolites in the conditioned fear and inhibitory avoidance tasks.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004 Jul;78(3):559-68. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2004.04.024. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004. PMID: 15251265
-
The testosterone metabolite and neurosteroid 3alpha-androstanediol may mediate the effects of testosterone on conditioned place preference.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Nov;37(1-3):162-71. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00116-3. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11744084 Review.
-
Androgen glucuronides analysis by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry: could it raise new perspectives in the diagnostic field of hormone-dependent malignancies?J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 1;940:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24140653 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in behavior, response to LPS, and glucose homeostasis in middle-aged mice.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 10;418:113628. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113628. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34687827 Free PMC article.
-
Androgens Enhance Recognition Memory and Dendritic Spine Density in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex of Ovariectomized Female Rats.Neuroscience. 2025 Mar 5;568:465-475. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 35671881
-
Endogenous testosterone levels are associated with assessments of unfavourable health information.Psychol Health. 2012;27(4):507-14. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2012.657639. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Psychol Health. 2012. PMID: 22348295 Free PMC article.
-
Anabolic/androgenic steroid administration during adolescence and adulthood differentially modulates aggression and anxiety.Horm Behav. 2015 Mar;69:132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Horm Behav. 2015. PMID: 25655668 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced stimulus sequence-dependent repeated learning in male offspring after prenatal stress alone or in conjunction with lead exposure.Neurotoxicology. 2012 Oct;33(5):1188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Neurotoxicology. 2012. PMID: 22796262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler A, Vescovo P, Robinson JK, Kritzer MF. Gonadectomy in adult life increases tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex and decreases open field activity in male mice. Neuroscience. 1999;89:939–954. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GM, Swerdloff RS, Wang C, Davidson T, McDonald V, Steiner B, et al. Androgen-behavior correlations in hypogonadal men and eugonadal men. II. Cognitive abilities. Horm Behav. 1998;33:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Beer TM, Bland LB, Bussiere JR, Neiss MB, Wersinger EM, Garzotto M, et al. Testosterone loss and estradiol administration modify memory in men. J Urol. 2006;175:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Bing O, Heilig M, Kakoulidis P, Sundblad C, Wikland L, Eriksson E. High doses of testosterone increase anti-conflict behavior in rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1998;8:321–323. - PubMed
-
- Bitran D, Kellog CK, Hilvers RJ. Treatment with an anabolic-androgenic steroid affects anxiety-related behavior and alters the sensitivity of cortical GABAA receptors in the rat. Horm Behav. 1993;27:568–583. - PubMed

