Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), p53 and MDM2 expression in Hodgkins disease
- PMID: 17625704
- PMCID: PMC11014697
- DOI: 10.1590/s1516-31802007000200003
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), p53 and MDM2 expression in Hodgkins disease
Abstract
Context and objective: Tumor cells in Hodgkins disease (HD) express cell proliferation markers that are evaluated according to the oncogenes involved or the expression of their proteins. Correlations between the protein expression grade and clinical data are now important for disease prognosis.
Design and setting: This was a retrospective analysis on proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), p53 and MDM2 (murine double minute-2) expression using immunohistochemistry, on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues from diagnostic biopsies on 51 patients with HD. The study was conducted at the Division of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine, Hospital São Paulo, Universidade Federal de São Paulo.
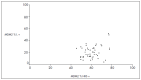
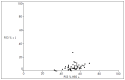
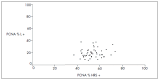
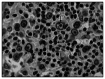
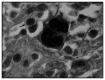
Methods: Antigen expression was evaluated as the proportions of positive Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells and reactive lymphocytes (L), which were compared using Spearman correlation coefficients. The Friedman test was used for comparisons between the markers. The Pearson test was used to investigate associations between marker expression and clinical and laboratory parameters, marrow involvement, complete remission (CR) and overall survival (OS) rates.
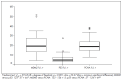
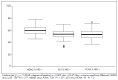
Results: There was overexpression of antigen proteins in HRS, in relation to L (p < 0.001). In HRS, MDM2 was higher than p53 and PCNA (p < 0.003), while the latter two were equivalent. In L, p53 was lower than MDM2 and PCNA (p < 0.001), while the latter two were equivalent. There was no relationship between protein expression and clinical and laboratory variables or outcome.
Conclusions: PCNA, p53 and MDM2 are tumor markers for HD, but showed no clinical or prognostic significance in our analysis.
CONTEXTO E OBJETIVO:: As células tumorais da doença de Hodgkin (HD) são positivas para marcadores de proliferação celular que são analisados por seus genes e respectivas proteínas. A correlação entre a expressão destas proteínas e os parâmetros clínico-laboratoriais são, no momento, de importância para o prognóstico da doença.
TIPO DE ESTUDO E LOCAL:: Estudo retrospectivo da expressão do antígeno de proliferação celular (PCNA) e da p53 e MDM2 em tecidos obtidos ao diagnóstico, fixados por formol, embebidos em parafina de 51 pacientes com HD. O trabalho foi realizado na Divisão de Hematologia e Transfusão, Hospital São Paulo, Universidade Federal de São Paulo.
MÉTODOS:: As expressões antigênicas foram analisadas através da proporção de células de Hodgkin e células de Reed Sternberg (HRS) e linfócitos reacionais (L) positivos. A intensidade de expressão de cada proteína foi comparada entre L e HRS através do coeficiente de Spearman. A comparação da PCNA, p53 e MDM2 em L e HRS se fez pelo teste de Fiedman. As correlações entre variáveis clínico-laboratoriais, comprometimento da medula óssea, taxas de sobrevida geral e remissão clínica com as proteínas em HRS se fizeram pelo coeficiente de Pearson.
RESULTADOS:: Houve superexpressão das três proteínas em células HRS comparadas aos L (p < 0,001). Nas células HRS, a MDM2 foi maior que a p53 e a PCNA (p < 0,003), que foram equivalentes. Nos L, a p53 foi menor que a MDM2 e a PCNA (p < 0,001), que foram equivalentes Não houve relação entre as expressões das proteínas com as variáveis clínico-laboratoriais e sobrevida.
CONCLUSÕES:: PCNA, p53 e MDM2 são marcadores tumorais na HD, porém não mostraram significado clínico-prognóstico em nossa análise.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spontaneous apoptosis of Reed-Sternberg and Hodgkin cells; clinical and pathological implications in patients with Hodgkin's disease.Int J Oncol. 2000 Sep;17(3):603-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.17.3.603. Int J Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10938405
-
Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and p53, bcl-2 or C-erb B-2 proteins on Reed-Sternberg cells: prognostic significance in Hodgkin's disease.Neoplasma. 1998;45(3):140-7. Neoplasma. 1998. PMID: 9717525
-
MDM2 and p53 expression in gliomas: a multivariate survival analysis including proliferation markers and epidermal growth factor receptor.Br J Cancer. 1997;75(9):1269-78. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.216. Br J Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9155045 Free PMC article.
-
The role of p53, MDM2 and c-erb B-2 oncoproteins, epidermal growth factor receptor and proliferation markers in the prognosis of urinary bladder cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 1997;193(11-12):767-75. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(97)80055-6. Pathol Res Pract. 1997. PMID: 9521509
-
[Expression of P21 WAF1/CIP1 in human astrocytomas in correlating with P53, MDM2, and cellular proliferation index].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2001 Aug;23(4):341-5. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2001. PMID: 12940073 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is a prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 28;9(1):e87474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087474. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24489919 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, molecular, and environmental risk factors for hodgkin lymphoma.Adv Hematol. 2011;2011:736261. doi: 10.1155/2011/736261. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Adv Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21127715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Falini B, Stein H, Pileri S, et al. Expression of lymphoid-associated antigens on Hodgkin’s and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin’s disease. An immunocytochemical study on lymph node cytospins using monoclonal antibodies. Histopathology. 1987;11(12):1229–1242. - PubMed
-
- Hsu SM, Hsu PL. Aberrant expression of T cell and B-cell markers in myelocyte/monocyte/histiocyte-derived lymphoma and leukemia cells. Is the infrequent expression of T/B cell markers sufficient to establish a lymphoid origin from Hodgkin’s Reed-Sternberg cells? Am J Pathol. 1989;134(1):203–212. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cossman J. Gene expression analysis of single neoplastic cells and the pathogenesis of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49(6):799–800. - PubMed
-
- Spieker T, Kurth J, Kuppers R, Rajewsky K, Bräuninger A, Hansmann ML. Molecular single-cell analysis of the clonal relationship of small Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells and Epstein-Barr virus-harboring Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin disease. Blood. 2000;96(9):3133–3138. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

