The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants
- PMID: 17626179
- PMCID: PMC1924592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705306104
The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants
Abstract
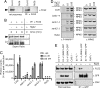
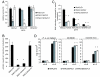
In pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI), plant cell surface receptors sense potential microbial pathogens by recognizing elicitors called PAMPs. Although diverse PAMPs trigger PTI through distinct receptors, the resulting intracellular responses overlap extensively. Despite this, a common component(s) linking signal perception with transduction remains unknown. In this study, we identify SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE (SERK)3/brassinosteroid-associated kinase (BAK)1, a receptor-like kinase previously implicated in hormone signaling, as a component of plant PTI. In Arabidopsis thaliana, AtSERK3/BAK1 rapidly enters an elicitor-dependent complex with FLAGELLIN SENSING 2 (FLS2), the receptor for the bacterial PAMP flagellin and its peptide derivative flg22. In the absence of AtSERK3/BAK1, early flg22-dependent responses are greatly reduced in both A. thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. Furthermore, N. benthamiana Serk3/Bak1 is required for full responses to unrelated PAMPs and, importantly, for restriction of bacterial and oomycete infections. Thus, SERK3/BAK1 appears to integrate diverse perception events into downstream PAMP responses, leading to immunity against a range of invading microbes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases BAK1/SERK3 and BKK1/SERK4 are required for innate immunity to hemibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens.Plant Cell. 2011 Jun;23(6):2440-55. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.084301. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21693696 Free PMC article.
-
The oomycete microbe-associated molecular pattern Pep-13 triggers SERK3/BAK1-independent plant immunity.Plant Cell Rep. 2019 Feb;38(2):173-182. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2359-5. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Plant Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30488097
-
A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence.Nature. 2007 Jul 26;448(7152):497-500. doi: 10.1038/nature05999. Epub 2007 Jul 11. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17625569
-
Assessing the diverse functions of BAK1 and its homologs in arabidopsis, beyond BR signaling and PTI responses.Mol Cells. 2013 Jan;35(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-2255-3. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Mol Cells. 2013. PMID: 23269431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A look at plant immunity through the window of the multitasking coreceptor BAK1.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017 Aug;38:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28458047 Review.
Cited by
-
Spermine inhibits PAMP-induced ROS and Ca2+ burst and reshapes the transcriptional landscape of PAMP-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2023 Jan 1;74(1):427-442. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac411. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36264272 Free PMC article.
-
BSK1, a receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, involved in both BR signaling and innate immunity in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Aug;8(8):e24996. doi: 10.4161/psb.24996. Epub 2013 May 20. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23733062 Free PMC article.
-
A highly-conserved single-stranded DNA-binding protein in Xanthomonas functions as a harpin-like protein to trigger plant immunity.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056240. Epub 2013 Feb 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23418541 Free PMC article.
-
Differential response of tomato genotypes to Xanthomonas-specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns and correlation with bacterial spot (Xanthomonas perforans) resistance.Hortic Res. 2016 Aug 10;3:16035. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2016.35. eCollection 2016. Hortic Res. 2016. PMID: 27555919 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic variation in two distinct Pseudomonas syringae flagellin epitopes modulates the strength of plant immune responses but not bacterial motility.New Phytol. 2013 Nov;200(3):847-860. doi: 10.1111/nph.12408. Epub 2013 Jul 19. New Phytol. 2013. PMID: 23865782 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

