Role of the primate amygdala in fear-potentiated startle: effects of chronic lesions in the rhesus monkey
- PMID: 17626199
- PMCID: PMC6672623
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5643-06.2007
Role of the primate amygdala in fear-potentiated startle: effects of chronic lesions in the rhesus monkey
Abstract
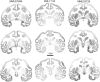
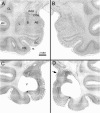
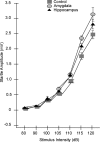
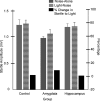
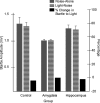
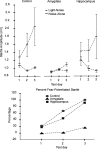
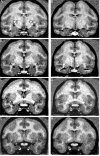
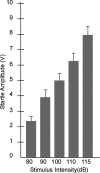
In experiment 1, we assessed the role of the primate amygdala and hippocampus in the acquisition of learned fear measured with fear-potentiated startle. Three groups of six rhesus monkeys were prepared with bilateral ibotenic acid lesions of the amygdaloid complex and the hippocampus or were sham operated. Selective ibotenic acid lesions of the amygdala, but not the hippocampus, blocked the acquisition of fear-potentiated startle. In experiment 2, we assessed the role of the primate amygdala in the expression of fear-potentiated startle. Surprisingly, animals that sustained amygdala damage after they successfully learned fear-potentiated startle expressed normal fear-potentiated startle, despite a complete amygdala lesion based on magnetic resonance imaging assessments. These results suggest that although the amygdala is necessary for the initial acquisition of fear-potentiated startle, it is not necessary for the retention and expression of fear-potentiated startle. These findings are discussed in relation to the role of the amygdala in emotional learning and in cross-species comparisons of emotional behavior.
Figures

References
-
- Aggleton JP, Passingham RE. Syndrome produced by lesions of the amygdala in monkeys (Macaca mulatta) J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1981;95:961–977. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Price JL, Pitkanen A, Carmichael T. Anatomical organization of the primate amygdaloid complex. In: Aggleton J, editor. The amygdala: neurobiological aspects of Emotion, memory, and mental dysfunction. New York: Wiley; 1992. pp. 1–66.
-
- Cassella J, Davis M. Habituation, prepulse inhibition, fear conditioning, and drug modulation of the acoustically elicited pinna reflex in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1986;100:39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
