Direct instrumental conditioning of neural activity using functional magnetic resonance imaging-derived reward feedback
- PMID: 17626211
- PMCID: PMC6672599
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2118-07.2007
Direct instrumental conditioning of neural activity using functional magnetic resonance imaging-derived reward feedback
Abstract
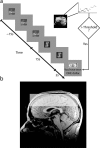
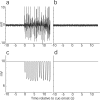
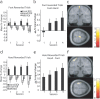
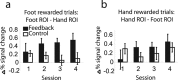
Successful learning is often contingent on feedback. In instrumental conditioning, an animal or human learns to perform specific responses to obtain reward. Instrumental conditioning is often used by behavioral psychologists to train an animal (or human) to produce a desired behavior. Shaping involves reinforcing those behaviors, which in a stepwise manner are successively closer to the desired behavior until the desired behavior is reached. Here, we aimed to extend this traditional approach to directly shape neural activity instead of overt behavior. To achieve this, we scanned 22 human subjects with functional magnetic resonance imaging and performed image processing in parallel with acquisition. We delineated regions of interest (ROIs) in finger and toe motor/somatosensory regions and used an instrumental shaping procedure to induce a regionally specific increase in activity by providing an explicit monetary reward to reinforce neural activity in the target areas. After training, we found a significant and regionally specific increase in activity in the ROI being rewarded (finger or toe) and a decrease in activity in the nonrewarded region. This demonstrates that instrumental conditioning procedures can be used to directly shape neural activity, even without the production of an overt behavioral response. This procedure offers an important alternative to traditional biofeedback-based approaches and may be useful in the development of future therapies for stroke and other brain disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Balleine BW, Dickinson A. Goal-directed instrumental action: contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology. 1998;37:407–419. - PubMed
-
- Birbaumer N, Kubler A, Ghanayim N, Hinterberger T, Perelmouter J, Kaiser J, Iversen I, Kotchoubey B, Neumann N, Flor H. The thought translation device (TTD) for completely paralyzed patients. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng. 2000;8:190–193. - PubMed
-
- Chen XY, Wolpaw JR. Operant-conditioning of H-reflex in freely moving rats. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:411–415. - PubMed
-
- Cox RW, Jesmanowicz A. Real-time 3D image registration for functional MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42:1014–1018. - PubMed
-
- Cox RW, Jesmanowicz A, Hyde JS. Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1995;33:230–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
