Lesions of the tegmentomammillary circuit in the head direction system disrupt the head direction signal in the anterior thalamus
- PMID: 17626218
- PMCID: PMC6672597
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0268-07.2007
Lesions of the tegmentomammillary circuit in the head direction system disrupt the head direction signal in the anterior thalamus
Abstract
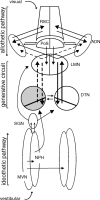
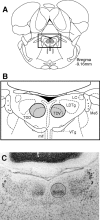
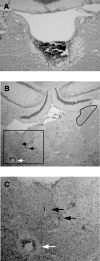
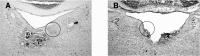
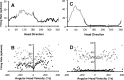
Head direction (HD) cells in the rodent limbic system are believed to correspond to a cognitive representation of directional heading in the environment. Lesions of vestibular hair cells disrupt the characteristic firing patterns of HD cells, and thus vestibular afference is a critical contributor to the HD signal. A subcortical pathway that may convey this information includes the dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden (DTN) and the lateral mammillary nucleus (LMN). To test the hypothesis that the DTN and LMN are critical components for generating HD cell activity, we made electrolytic lesions of the DTN or LMN in rats and screened for HD cell activity in the anterior thalamus. Directional activity was absent in all animals with complete LMN lesions and in animals with complete DTN lesions, although a few HD cells were isolated in animals with incomplete lesions. Some DTN-lesioned animals contained cells whose firing rates were modulated by angular head velocity. Although cells with bursting patterns of activity have been observed in the anterior dorsal nucleus of the thalamus of animals with disruption of vestibular inputs, this pattern of activity was not observed in either the LMN- or DTN-lesioned animals. The general absence of direction-specific activity in the anterior thalamus of animals with DTN or LMN lesions is consistent with the view that the DTN-LMN circuit is essential for the generation of HD cell activity.
Figures

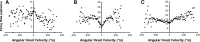


Similar articles
-
Neural correlates for angular head velocity in the rat dorsal tegmental nucleus.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 1;21(15):5740-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05740.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11466446 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the lateral mammillary nucleus in the rat head direction circuit: a combined single unit recording and lesion study.Neuron. 1998 Dec;21(6):1387-97. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80657-1. Neuron. 1998. PMID: 9883731
-
The anterior thalamic head-direction signal is abolished by bilateral but not unilateral lesions of the lateral mammillary nucleus.J Neurosci. 1999 Aug 1;19(15):6673-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06673.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10414996 Free PMC article.
-
The anatomical and computational basis of the rat head-direction cell signal.Trends Neurosci. 2001 May;24(5):289-94. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01797-5. Trends Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11311382 Review.
-
Persistent neural activity in head direction cells.Cereb Cortex. 2003 Nov;13(11):1162-72. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhg102. Cereb Cortex. 2003. PMID: 14576208 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial navigation. Disruption of the head direction cell network impairs the parahippocampal grid cell signal.Science. 2015 Feb 20;347(6224):870-874. doi: 10.1126/science.1259591. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Science. 2015. PMID: 25700518 Free PMC article.
-
Remembered reward locations restructure entorhinal spatial maps.Science. 2019 Mar 29;363(6434):1447-1452. doi: 10.1126/science.aav5297. Science. 2019. PMID: 30923222 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-binding protein immunoreactivity in Gudden's tegmental nuclei and the hippocampal formation: differential co-localization in neurons projecting to the mammillary bodies.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Aug 4;9:103. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00103. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 26300741 Free PMC article.
-
Non-rhythmic head-direction cells in the parahippocampal region are not constrained by attractor network dynamics.Elife. 2018 Sep 17;7:e35949. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35949. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30222110 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal premammillary projection to periaqueductal gray controls escape vigor from innate and conditioned threats.Elife. 2021 Sep 1;10:e69178. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69178. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34468312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen GV, Hopkins DA. Mamillary body in the rat: topography and synaptology of projections from the subicular complex, prefrontal cortex, and midbrain tegmentum. J Comp Neurol. 1989;286:311–336. - PubMed
-
- Allen GV, Hopkins DA. Topography and synaptology of mamillary body projections to the mesencephalon and pons in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990;301:214–231. - PubMed
-
- Bassett JP, Taube JS. Head direction signal generation: ascending and descending information streams. In: Wiener SI, Taube JS, editors. Head direction cells and the neural mechanisms of spatial orientation. Cambridge, MA: MIT; 2005. pp. 83–109.
-
- Batschelet E. New York: Academic; 1981. Circular statistics in biology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
