Type II restriction endonuclease R.Eco29kI is a member of the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily
- PMID: 17626614
- PMCID: PMC1952068
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-48
Type II restriction endonuclease R.Eco29kI is a member of the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily
Abstract
Background: The majority of experimentally determined crystal structures of Type II restriction endonucleases (REases) exhibit a common PD-(D/E)XK fold. Crystal structures have been also determined for single representatives of two other folds: PLD (R.BfiI) and half-pipe (R.PabI), and bioinformatics analyses supported by mutagenesis suggested that some REases belong to the HNH fold. Our previous bioinformatic analysis suggested that REase R.Eco29kI shares sequence similarities with one more unrelated nuclease superfamily, GIY-YIG, however so far no experimental data were available to support this prediction. The determination of a crystal structure of the GIY-YIG domain of homing endonuclease I-TevI provided a template for modeling of R.Eco29kI and prompted us to validate the model experimentally.
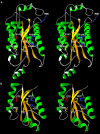
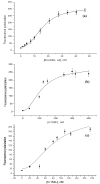
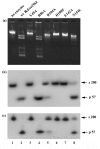
Results: Using protein fold-recognition methods we generated a new alignment between R.Eco29kI and I-TevI, which suggested a reassignment of one of the putative catalytic residues. A theoretical model of R.Eco29kI was constructed to illustrate its predicted three-dimensional fold and organization of the active site, comprising amino acid residues Y49, Y76, R104, H108, E142, and N154. A series of mutants was constructed to generate amino acid substitutions of selected residues (Y49A, R104A, H108F, E142A and N154L) and the mutant proteins were examined for their ability to bind the DNA containing the Eco29kI site 5'-CCGCGG-3' and to catalyze the cleavage reaction. Experimental data reveal that residues Y49, R104, E142, H108, and N154 are important for the nuclease activity of R.Eco29kI, while H108 and N154 are also important for specific DNA binding by this enzyme.
Conclusion: Substitutions of residues Y49, R104, H108, E142 and N154 predicted by the model to be a part of the active site lead to mutant proteins with strong defects in the REase activity. These results are in very good agreement with the structural model presented in this work and with our prediction that R.Eco29kI belongs to the GIY-YIG superfamily of nucleases. Our study provides the first experimental evidence for a Type IIP REase that does not belong to the PD-(D/E)XK or HNH superfamilies of nucleases, and is instead a member of the unrelated GIY-YIG superfamily.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Type II restriction endonuclease R.Hpy188I belongs to the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily, but exhibits an unusual active site.BMC Struct Biol. 2008 Nov 14;8:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-8-48. BMC Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 19014591 Free PMC article.
-
A homology model of restriction endonuclease SfiI in complex with DNA.BMC Struct Biol. 2005 Jan 24;5:2. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-5-2. BMC Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 15667656 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and evolutionary classification of Type II restriction enzymes based on theoretical and experimental analyses.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jun;36(11):3552-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn175. Epub 2008 May 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18456708 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallographic and bioinformatic studies on restriction endonucleases: inference of evolutionary relationships in the "midnight zone" of homology.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003 Oct;4(5):327-37. doi: 10.2174/1389203033487072. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003. PMID: 14529527 Review.
-
Catalytic mechanisms of restriction and homing endonucleases.Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 26;41(47):13851-60. doi: 10.1021/bi020467h. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12437341 Review.
Cited by
-
Tetrameric structure of the restriction DNA glycosylase R.PabI in complex with nonspecific double-stranded DNA.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:35197. doi: 10.1038/srep35197. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731370 Free PMC article.
-
Structural, functional and evolutionary relationships between homing endonucleases and proteins from their host organisms.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(12):5189-200. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks226. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22406833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fused eco29kIR- and M genes coding for a fully functional hybrid polypeptide as a model of molecular evolution of restriction-modification systems.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Feb 3;11:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-35. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21291520 Free PMC article.
-
Rational engineering of sequence specificity in R.MwoI restriction endonuclease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8579-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks570. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22735699 Free PMC article.
-
Hpy188I-DNA pre- and post-cleavage complexes--snapshots of the GIY-YIG nuclease mediated catalysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Mar;39(4):1554-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq821. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20935048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pingoud AM. Restriction endonucleases. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg; 2004.
-
- Sapranauskas R, Sasnauskas G, Lagunavicius A, Vilkaitis G, Lubys A, Siksnys V. Novel subtype of type IIs restriction enzymes. BfiI endonuclease exhibits similarities to the EDTAresistant nuclease Nuc of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:30878–30885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003350200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

