Role of adenosine A3 receptors on CA1 hippocampal neurotransmission during oxygen-glucose deprivation episodes of different duration
- PMID: 17626785
- PMCID: PMC2000832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.06.003
Role of adenosine A3 receptors on CA1 hippocampal neurotransmission during oxygen-glucose deprivation episodes of different duration
Abstract
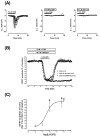
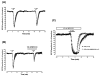
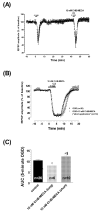
The role of adenosine A3 receptors in synaptic transmission under severe (7 min) and shorter (2-5 min) ischemic conditions, obtained by oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD), was investigated in rat hippocampal slices. The effects of selective A3 agonists or antagonists were examined on field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) extracellularly recorded at the dendritic level of the CA1 pyramidal region. The novel, selective A3 antagonist LJ1251 ((2R,3R,4S)-2-(2-chloro-6-(3-iodobenzylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl)tetrahydrothiophene-3,4-diol, 0.1-10 nM) protected hippocampal slices from irreversible fEPSP depression induced by severe OGD and prevented or delayed the appearance of anoxic depolarization. Similar results were obtained when severe OGD was carried out with a long, receptor-desensitizing exposure to various selective A3 agonists: 5'-N-methylcarboxamidoadenosine derivatives Cl-IB-MECA (N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-2-chloro), VT72 (N6-methoxy-2-phenylethynyl), VT158 (N6-methoxy-2-phenylethynyl), VT160 (N6-methoxy-2-(2-pyridinyl)-ethynyl), and VT163 (N6-methoxy-2-p-acetylphenylethynyl) and AR132 (N6-methyl-2-phenylethynyladenosine). The selective A3 antagonist MRS1523 (3-propyl-6-ethyl-5-[(ethylthio)carbonyl]-2-phenyl-4-propyl-3-pyridine carboxylate, 100 nM) reduced fEPSP depression evoked by 2-min OGD and induced a faster recovery of fEPSP amplitude after 5-min OGD. Similar results were obtained for 2- or 5-min OGD applied in the presence of each of the A3 agonists tested. Shorter exposure to A3 agonists significantly delayed the recovery of fEPSP amplitude after 5-min OGD. This indicates that A3 receptors, stimulated by selective A3 agonists, undergo desensitization during OGD. It is inferred that CA1 hippocampal A3 receptors stimulated by adenosine released during brief ischemia (2 and 5 min) might exert A1-like protective effects on neurotransmission. Severe ischemia would transform the A3 receptor-mediated effects from protective to injurious.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy.Med Res Rev. 2018 Jul;38(4):1031-1072. doi: 10.1002/med.21456. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 28682469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A3 adenosine receptor antagonists delay irreversible synaptic failure caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation in the rat CA1 hippocampus in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;147(5):524-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706646. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16415905 Free PMC article.
-
Brief, repeated, oxygen-glucose deprivation episodes protect neurotransmission from a longer ischemic episode in the in vitro hippocampus: role of adenosine receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Sep;140(2):305-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705442. Epub 2003 Aug 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12970092 Free PMC article.
-
The adenosine A2A receptor antagonist ZM241385 enhances neuronal survival after oxygen-glucose deprivation in rat CA1 hippocampal slices.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jul;157(5):818-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00218.x. Epub 2009 May 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19422385 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the adenosinergic system in lung fibrosis.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Oct;76:182-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23994158 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of ADORA3 promotes microglial phagocytosis and alleviates chronic ischemic white matter injury.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 May;30(5):e14742. doi: 10.1111/cns.14742. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38715283 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine and stroke: maximizing the therapeutic potential of adenosine as a prophylactic and acute neuroprotectant.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009 Sep;7(3):217-27. doi: 10.2174/157015909789152209. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20190963 Free PMC article.
-
The A3 adenosine receptor attenuates the calcium rise triggered by NMDA receptors in retinal ganglion cells.Neurochem Int. 2010 Jan;56(1):35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.08.011. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Neurochem Int. 2010. PMID: 19723551 Free PMC article.
-
A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy.Med Res Rev. 2018 Jul;38(4):1031-1072. doi: 10.1002/med.21456. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 28682469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective block of adenosine A2A receptors prevents ischaemic-like effects induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat medium spiny neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Oct;179(20):4844-4856. doi: 10.1111/bph.15922. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35817954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diaz-Hernandez M, Pereira MF, Pintor J, Cunha RA, Ribeiro JA, Miras-Portugal MT. Modulation of the rat hippocampal dinucleotide receptor by adenosine receptor activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;301:441–450. - PubMed
-
- Lopes LV, Rebola N, Pinheiro PC, Richardson PJ, Oliveira CR, Cunha RA. Adenosine A3 receptors are located in neurons of the rat hippocampus. Neuroreport. 2003;14:1645–1648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

