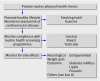
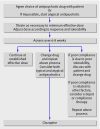
Schizophrenia
- PMID: 17626963
- PMCID: PMC1914490
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39227.616447.BE
Schizophrenia
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hanssen M, Bak M, Bijl R, Vollebergh W, van Os J. The incidence and outcome of subclinical psychotic experiences in the general population. Br J Clin Psychol 2005;44:181-91. - PubMed
-
- Jablensky A. Epidemiology of schizophrenia: the global burden of disease and disability. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2000;250:274-85. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen CB, Mortensen PB. Evidence of a dose-response relationship between urbanicity during upbringing and schizophrenia risk. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001;58:1039-46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical