2-Amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-[4,5-f]quinoxaline-induced DNA adduct formation and mutagenesis in DNA repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing human cytochrome P4501A1 and rapid or slow acetylator N-acetyltransferase 2
- PMID: 17627018
- PMCID: PMC2135550
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0305
2-Amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-[4,5-f]quinoxaline-induced DNA adduct formation and mutagenesis in DNA repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing human cytochrome P4501A1 and rapid or slow acetylator N-acetyltransferase 2
Abstract
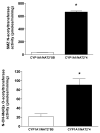
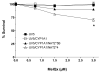
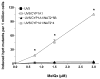
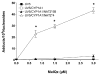
2-Amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) is one of the most potent and abundant mutagens in the western diet. Bioactivation includes N-hydroxylation catalyzed by cytochrome P450s followed by O-acetylation catalyzed by N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2). In humans, NAT2*4 allele is associated with rapid acetylator phenotype, whereas NAT2*5B allele is associated with slow acetylator phenotype. We hypothesized that rapid acetylator phenotype predisposes humans to DNA damage and mutagenesis from MeIQx. Nucleotide excision repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells were constructed by stable transfection of human cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1) and a single copy of either NAT2*4 (rapid acetylator) or NAT2*5B (slow acetylator) alleles. CYP1A1 and NAT2 catalytic activities were undetectable in untransfected Chinese hamster ovary cell lines. CYP1A1 activity did not differ significantly (P > 0.05) among the CYP1A1-transfected cell lines. Cells transfected with NAT2*4 had 20-fold significantly higher levels of sulfamethazine N-acetyltransferase (P = 0.0001) and 6-fold higher levels of N-hydroxy-MeIQx O-acetyltransferase (P = 0.0093) catalytic activity than cells transfected with NAT2*5B. Only cells transfected with both CYP1A1 and NAT2*4 showed concentration-dependent cytotoxicity and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase mutagenesis following MeIQx treatment. Deoxyguanosine-C8-MeIQx was the primary DNA adduct formed and levels were dose dependent in each cell line and in the following order: untransfected < transfected with CYP1A1 < transfected with CYP1A1 and NAT2*5B < transfected with CYP1A1 and NAT2*4. MeIQx DNA adduct levels were significantly higher (P < 0.001) in CYP1A1/NAT2*4 than CYP1A1/NAT2*5B cells at all concentrations of MeIQx tested. MeIQx-induced DNA adduct levels correlated very highly (r2 = 0.88) with MeIQx-induced mutants. These results strongly support extrahepatic activation of MeIQx by CYP1A1 and a robust effect of human NAT2 genetic polymorphism on MeIQx-induced DNA adducts and mutagenesis. The results provide laboratory-based support for epidemiologic studies reporting higher frequency of heterocyclic amine-related cancers in rapid NAT2 acetylators.
Figures


References
-
- Keating GA, Bogen KT. Estimates of heterocyclic amine intake in the US population. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2004;802:127–33. - PubMed
-
- Byrne C, Sinha R, Platz EA, et al. Predictors of dietary heterocyclic amine intake in three prospective cohorts. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998;7:523–9. - PubMed
-
- National Toxicology Program. Report on Carcinogenesis. 11. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Research; Triangle Park, NC: 2005.
-
- Ohgaki H, Hasegawa H, Suenaga M, Sato S, Takayama S, Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity in mice of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) from cooked foods. Carcinogenesis. 1987;8:665–8. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Ohgaki H, Hasegawa H, Sato S, Takayama S, Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity in rats of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline. Carcinogenesis. 1988;9:71–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

