Ethanol augments PDGF-induced NADPH oxidase activity and proliferation in rat pancreatic stellate cells
- PMID: 17627098
- PMCID: PMC2826430
- DOI: 10.1159/000105499
Ethanol augments PDGF-induced NADPH oxidase activity and proliferation in rat pancreatic stellate cells
Abstract
Background/aims: Activated stellate cells are considered the principal mediators of chronic alcoholic pancreatitis/fibrosis. However the mechanisms of alcohol action on pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are poorly understood. The aims of this study were to determine the presence and role of the NADPH oxidase system in mediating alcohol effects on PaSCs with specific emphasis on proliferation.
Methods: PaSC NADPH oxidase components mRNA and protein were determined by RT-PCR and Western blot. The NADPH oxidase activity was measured by detecting the production of reactive oxygen species using lucigenin-derived chemiluminescence assay. PaSC DNA synthesis, a measure of proliferation, was performed by determining the [3H] thymidine incorporation into DNA.
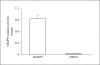
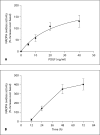
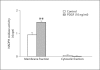
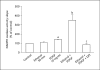
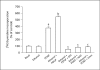
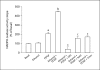
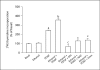
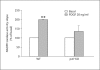
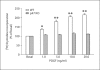
Results: mRNA for NADPH oxidase components Nox1, gp91(phox), Nox4, p22(phox), p47(phox) and p67(phox) and protein for NADPH oxidase subunits gp91(phox), p22(phox), p47(phox) and p67(phox) are present in PaSCs. Treatment with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) significantly increased the NADPH oxidase activity and DNA synthesis in cultured PaSCs. Alcohol treatment markedly augmented both the NADPH oxidase activity and the DNA synthesis caused by PDGF, which was prevented by antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine, ROS scavenger tiron, and the NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenylene iodium. The effects of PDGF on NADPH oxidase activity and DNA synthesis were prevented in PaSCs isolated from the pancreas of mice with a genetic deficiency of p47(phox).
Conclusions: Ethanol causes proliferation of stellate cells by augmenting the activation of the cell's NADPH oxidase system stimulated by PDGF. These results provide new insights into the mechanisms of alcohol-induced fibrosing disorders.
2007 S. Karger AG, Basel and IAP
Figures


Similar articles
-
NADPH oxidase plays a crucial role in the activation of pancreatic stellate cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008 Jan;294(1):G99-G108. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00272.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008. PMID: 17962358
-
Temporal changes in the expression of mRNA of NADPH oxidase subunits in renal epithelial cells exposed to oxalate or calcium oxalate crystals.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Jun;26(6):1778-85. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq692. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21079197 Free PMC article.
-
Bioluminescence imaging of NADPH oxidase activity in different animal models.J Vis Exp. 2012 Oct 22;(68):3925. doi: 10.3791/3925. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 23117583 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils: Role of the phosphorylation of its subunits.Eur J Clin Invest. 2018 Nov;48 Suppl 2:e12951. doi: 10.1111/eci.12951. Epub 2018 Jun 3. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29757466 Review.
-
Role of the small GTPase Rac in p22phox-dependent NADPH oxidases.Biochimie. 2007 Sep;89(9):1133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 May 17. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17583407 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological stimulation of NQO1 decreases NADPH levels and ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Dec 18;10(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1252-z. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30584237 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol consumption as inductor of pancreatitis.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Feb 6;1(1):3-8. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v1.i1.3. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 21577288 Free PMC article.
-
The burning question: why is smoking a risk factor for pancreatic cancer?Pancreatology. 2012 Jul-Aug;12(4):344-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Pancreatology. 2012. PMID: 22898636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of NADPH oxidases in liver fibrosis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jun 10;20(17):2854-72. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5619. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24040957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steamed daylily flower (Hemerocallis fulva L.) protected cardiac and hepatic cells against ethanol induced apoptotic and oxidative damage.J Food Drug Anal. 2023 Dec 15;31(4):649-663. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3485. J Food Drug Anal. 2023. PMID: 38526821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P, Cavallini G, Ammann RW, Lankisch PG, Andersen JR, Dimagno EP, Andren-Sandberg A, Domellof L. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer. International Pancreatitis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1433–1437. - PubMed
-
- Apte MV, Phillips PA, Fahmy RG, Darby SJ, Rodgers SC, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Naidoo D, Wilson JS. Does alcohol directly stimulate pancreatic fibrogenesis? Studies with rat pancreatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:780–794. - PubMed
-
- Adachi T, Togashi H, Suzuki A, Kasai S, Ito J, Sugahara K, Kawata S. NAD(P)H oxidase plays a crucial role in PDGF-induced proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2005;41:1272–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

