Efficacy of dosing and re-dosing of two oral fixed combinations of indomethacin, prochlorperazine and caffeine compared with oral sumatriptan in the acute treatment of multiple migraine attacks: a double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, parallel group, multicentre study
- PMID: 17627707
- PMCID: PMC1974802
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01458.x
Efficacy of dosing and re-dosing of two oral fixed combinations of indomethacin, prochlorperazine and caffeine compared with oral sumatriptan in the acute treatment of multiple migraine attacks: a double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, parallel group, multicentre study
Abstract
Aims and methods: In this double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, parallel group, multicentre study, the efficacy of dosing and re-dosing of a fixed combination of indomethacin, prochlorperazine and caffeine (Indoprocaf) was compared with encapsulated sumatriptan in the acute treatment of two migraine attacks. Additionally, in the group taking Indoprocaf, two different oral formulations were tested: effervescent tablets and encapsulated coated tablets.
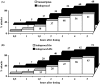
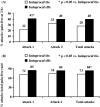
Results: Of 297 patients randomised (150 assigned to Indoprocaf and 147 to sumatriptan), 281 were included in the intention-to-treat efficacy analysis. The initial dosing of Indoprocaf and sumatriptan was similarly effective with pain-free rates higher than 30% (95% CI of odds-ratio: 0.57-1.28) and headache relief rates of about 60% (95% CI of odds-ratio: 0.82-1.84) with both the drugs. The efficacy of re-dosing of Indoprocaf as rescue medication was more effective than that of sumatriptan with pain-free values of 47% vs. 27% in the total attacks with a statistically significant difference in the first migraine attack in favour of Indoprocaf. The efficacy of re-dosing to treat a recurrence/relapse was very high without differences between the drugs (pain-free: 60% with Indoprocaf and 50% with sumatriptan in the total attacks). Indoprocaf and sumatriptan were well-tolerated.
Conclusion: The study demonstrated that the efficacy of the initial dosing of Indoprocaf was not higher than that of sumatriptan, but that the strategy to use the lowest effective dose as soon as the headache occurred, followed by a second dose if the headache has not relieved or to treat a relapse, was very effective, especially with Indoprocaf.
Figures
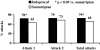

References
-
- Sicuteri F. The holistic hypothesis of migraine. Ann Ital Med Int. 1997;12(Suppl. 1):1S–32S.
-
- Hu XH. Central mechanism of indomethacin analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;263:53–7. - PubMed
-
- Akerman S. The effect of anti-migraine compounds on nitric oxide-induced dilation of dural meningeal vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;452:223–8. - PubMed
-
- Tassorelli C. The effects on the central nervous system of nitroglycerin - Putative mechanisms and mediators. Prog Neurobiol. 1999;57:607–24. - PubMed
-
- Jurna I. Central effect of the non-steroid anti-inflammatory agents, indomethacin, ibuprofen, and diclofenac, determined in C fibre-evoked activity in single neurones of the rat thalamus. Pain. 1990;41:71–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

