Identification and characterization of juvenile hormone esterase gene from the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- PMID: 17628281
- PMCID: PMC2020842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2007.05.010
Identification and characterization of juvenile hormone esterase gene from the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
Abstract
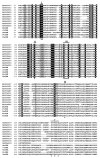
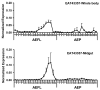
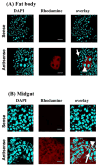
Juvenile hormone esterase (JHE) plays an important role in regulating juvenile hormone titers. Recent sequencing and annotation of the Aedes aegypti genome identified ten putative jhe gene sequences. Analysis of these ten putative jhe gene sequences showed that only three of them, EAT43357, EAT43353 and EAT43354 contained GQSAG motif and showed high sequence similarity with the sequences of jhe genes identified from other insect species. To determine which putative jhe gene(s) code for functional JHE, the mRNA profiles of EAT43357, EAT43353 and EAT43354 were measured during the final instar larval and pupal stages by using quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The mRNA for EAT43357 was detected during the late final instar larval stage. In contrast, EAT43354 mRNA was detected only during the pupal stage and EAT43353 mRNA was detected only during the larval stage. The mRNA of EAT43357 was detected in both fat body and midgut tissues. JHE enzyme levels gradually increased during the final instar larval stage reaching a peak at 42 h after ecdysis into the final instar larval stage. The mRNA expression profiles of EAT43357 correlate with the developmental expression profiles of JHE enzyme activity suggesting that this gene may encode for a functional JHE. The EAT43357 and EAT43354 cDNA were expressed in a baculovirus system. Proteins isolated from Sf9 cells infected with recombinant baculovirus expressing EAT43357 but not EAT43354 gene exhibited JHE activity confirming that EAT43357 gene codes for a functional JHE enzyme.
Figures




References
-
- Bonning BC, Hoover K, Booth TF, Duffey S, Hammock BD. Development of a recombinant baculovirus expressing a modified juvenile hormone esterase with potential for insect control. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1995;30:177–194.
-
- Bradford MM. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PM, Harcourt RL, Crone EJ, Claudianos C, Hammock BD, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG. Identification of a juvenile hormone esterase gene by matching its peptide mass fingerprint with a sequence from the Drosophila genome project. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;31:513–520. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PM, Healy MJ, Oakeshott JG. Characterization of juvenile hormone esterase in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;22:665–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

