The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 does not modify methamphetamine reinstatement of responding
- PMID: 17628534
- PMCID: PMC2148070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.06.004
The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 does not modify methamphetamine reinstatement of responding
Abstract
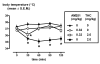
Cannabinoid CB(1) receptor antagonists can decrease methamphetamine self-administration. This study examined whether the CB(1) receptor antagonist AM251 [N-(piperidin-1-yl)-5-(4-indophonyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide] modifies reinstatement in rats that previously self-administered methamphetamine. Rats (n=10) self-administered methamphetamine (0.1 mg/kg/infusion) under a fixed ratio 2 schedule. Non-contingent methamphetamine (0.01-1.78 mg/kg, i.v.) yielded responding for saline (reinstatement) that was similar to responding for self-administered methamphetamine. AM251 (0.032-0.32, i.v.) did not affect methamphetamine-induced reinstatement but significantly attenuated Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (2.0 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced hypothermia. These data fail to support a role for endogenous cannabinoids or cannabinoid CB(1) receptors in reinstatement and, therefore, relapse to stimulant abuse.
Figures
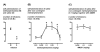
Similar articles
-
Local pretreatment with the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 attenuates methamphetamine intra-accumbens self-administration.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Feb 11;489(3):187-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.12.013. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21167256 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the relative potency of SR 141716A and AM 251 as antagonists of various in vivo effects of cannabinoid agonists in C57BL/6J mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Aug 13;569(1-2):70-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.04.054. Epub 2007 May 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17553486 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of cannabinoid CB1, CB2 and vanilloid TRPV1 receptor antagonists on cocaine addictive behavior in rats.Brain Res. 2012 Mar 20;1444:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.01.030. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22325096
-
Methamphetamine-seeking behavior is due to inhibition of nicotinic cholinergic transmission by activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Dec;55(8):1300-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.012. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18782581
-
(R)-Methanandamide and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced operant rate decreases in rats are not readily antagonized by SR-141716A.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Apr 11;466(1-2):121-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01491-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12679148
Cited by
-
Effects of cannabinoid receptor antagonists on maintenance and reinstatement of methamphetamine self-administration in rhesus monkeys.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 May 10;633(1-3):44-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.02.005. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20153314 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Treatments for Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Current Status and Future Targets.Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2024 Aug 30;15:125-161. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S431273. eCollection 2024. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 39228432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothesis-driven medication discovery for the treatment of psychostimulant addiction.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008 Nov;1(3):303-27. doi: 10.2174/1874473710801030303. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008. PMID: 19430578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local pretreatment with the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 attenuates methamphetamine intra-accumbens self-administration.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Feb 11;489(3):187-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.12.013. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21167256 Free PMC article.
-
Racemic gamma vinyl-GABA (R,S-GVG) blocks methamphetamine-triggered reinstatement of conditioned place preference.Synapse. 2009 Feb;63(2):87-94. doi: 10.1002/syn.20582. Synapse. 2009. PMID: 19016239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anggadiredja K, Nakamichi M, Hiranita T, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Watanabe S, Yamamoto T. Endocannabinoid system modulates relapse to methamphetamine seeking: possible mediation by the arachidonic acid cascade. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004a;29:470–1478. - PubMed
-
- Anggadiredga K, Sakimura K, Hiranita T, Yamanoto T. Naltrexone attenuates cue- but not drug-induced methamphetamine seeking: a possible mechanism for the dissociation of primary and secondary reward. Brain Res. 2004b;24:272–276. - PubMed
-
- Bray GA. Use and abuse of appetite-suppressant drugs in the treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1993;119:707–713. - PubMed
-
- Cippitelli A, Bilbao A, Hansson AC, del Arco I, Sommer W, Heilig M, Massi M, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Navarro M, Ciccocioppo R, de Fonseca FR The European TARGALC Consortium. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonism reduced conditioned reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:2243–2251. - PubMed
-
- De Vries TJ, Shaham Y, Homberg JR, Crombag H, Schuurman K, Dieben J, Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN. A cannabinoid mechanism in relapse to cocaine seeking. Nat Med. 2001;7:1151–1154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

