p53 mediates interstitial cystitis antiproliferative factor (APF)-induced growth inhibition of human urothelial cells
- PMID: 17628545
- PMCID: PMC1939966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.06.058
p53 mediates interstitial cystitis antiproliferative factor (APF)-induced growth inhibition of human urothelial cells
Abstract
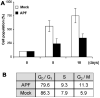
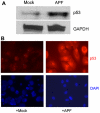
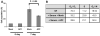
Antiproliferative factor (APF) is a sialoglycopeptide elevated in the urine of patients with interstitial cystitis, a urinary bladder disorder of unknown etiology that is characterized by chronic pelvic pain. The present study was directed toward uncovering a pathway through which APF signals. Treatment of human urothelial cells with native APF resulted in growth inhibition accompanied by blockade of cell cycle transit and increased p53. Reduced expression of p53 by RNA interference diminished, while ectopic expression of p53 mimicked, the effects of APF. These are the first findings implicating the network of p53 target genes in urothelial defects associated with interstitial cystitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A synthetic form of frizzled 8-associated antiproliferative factor enhances p53 stability through USP2a and MDM2.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050392. Epub 2012 Dec 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236372 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics identifies a beta-catenin network as an element of the signaling response to Frizzled-8 protein-related antiproliferative factor.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Jun;10(6):M110.007492. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.007492. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21422242 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative factor regulates connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) expression in T24 bladder carcinoma cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(10):1976-85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0714. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22438586 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunction of bladder urothelium and bladder urothelial cells in interstitial cystitis.Curr Urol Rep. 2006 Nov;7(6):440-6. doi: 10.1007/s11934-006-0051-8. Curr Urol Rep. 2006. PMID: 17052438 Review.
-
Update on Urinary Tract Markers in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):16-23. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0000000000000224. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2016. PMID: 26571430 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome with and without Hunner Lesion: A Review and Future Perspectives.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;11(12):2238. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122238. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioglitazone Alters the Proteomes of Normal Bladder Epithelial Cells but Shows No Tumorigenic Effects.Int Neurourol J. 2020 Mar;24(1):29-40. doi: 10.5213/inj.1938186.093. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Int Neurourol J. 2020. PMID: 32252184 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 23;10(10):2380. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102380. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiproliferative factor decreases Akt phosphorylation and alters gene expression via CKAP4 in T24 bladder carcinoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 10;29(1):160. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-160. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21143984 Free PMC article.
-
Short and sweet: evolution of a small glycopeptide from a bladder disorder to an anticancer lead.Mol Interv. 2009 Feb;9(1):14-7. doi: 10.1124/mi.9.1.5. Mol Interv. 2009. PMID: 19299659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogart LM, Berry SH, Clemens JQ. Symptoms of interstitial cystitis, painful bladder syndrome and similar diseases in women: a systematic review. J. Urol. 2007;177:450–456. - PubMed
-
- Keay S, et al. Concentrations of specific epithelial growth factors in the urine of interstitial cystitis patients and controls. J. Urol. 1997;158:1983–1988. - PubMed
-
- Keay S, et al. A diagnostic in vitro urine assay for interstitial cystitis. Urology. 1998;52:974–978. - PubMed
-
- Keay S, Zhang CO, Marvel R, Chai T. Antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor: sensitive and specific urine markers for interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2001;57:104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

