Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis: mechanism and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 17629468
- PMCID: PMC2754308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.05.004
Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis: mechanism and therapeutic potential
Abstract
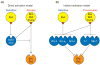
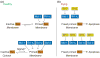
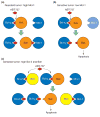
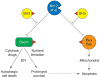
Apoptosis is essential for tissue homeostasis, particularly in the hematopoietic compartment, where its impairment can elicit neoplastic or autoimmune diseases. Whether stressed cells live or die is largely determined by interplay between opposing members of the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 and its closest homologs promote cell survival, but two other factions promote apoptosis. The BH3-only proteins sense and relay stress signals, but commitment to apoptosis requires Bax or Bak. The BH3-only proteins appear to activate Bax and Bak indirectly, by engaging and neutralizing their pro-survival relatives, which otherwise constrain Bax and Bak from permeabilizing mitochondria. The Bcl-2 family may also regulate autophagy and mitochondrial fission/fusion. Its pro-survival members are attractive therapeutic targets in cancer and perhaps autoimmunity and viral infections.
Figures
References
-
- Strasser A. The role of BH3-only proteins in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:189–200. This recent review clearly outlines the physiological roles of the Bcl-2 family and apoptosis, particularly in the immune system. - PubMed
-
- Adams JM. Ways of dying: multiple pathways to apoptosis. Genes Dev. 2003;17:2481–2495. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y. Mechanical aspects of apoptosome assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:677–684. - PubMed
-
- Hinds MG, Day CL. Regulation of apoptosis: uncovering the binding determinants. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005;15:690–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

