Pathways regulating apoptosis during patterning and development
- PMID: 17629474
- PMCID: PMC1989756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.05.009
Pathways regulating apoptosis during patterning and development
Abstract
The patterning and development of multicellular organisms require a precisely controlled balance between cell proliferation, differentiation and death. The regulation of apoptosis is an important aspect to achieve this balance, by eliminating unnecessary or mis-specified cells which, otherwise, may have harmful effects on the whole organism. Apoptosis is also important for the morphogenetic processes that occur during development and that lead to the sculpting of organs and other body structures. Here, we review recent progress in understanding how apoptosis is regulated during development, focusing on studies using Drosophila or Caenorhabditis elegans as model organisms.
Figures
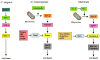
References
-
- Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. - PubMed
-
- Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death in development. Cell. 1999;96:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Song Z, Steller H. Death by design: mechanism and control of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:M49–52. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann SH, Hengartner MO. Programmed cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:526–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

