Dopamine receptor activation reveals a novel, kynurenate-sensitive component of striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity
- PMID: 17629627
- PMCID: PMC2034343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.033
Dopamine receptor activation reveals a novel, kynurenate-sensitive component of striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity
Abstract
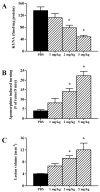
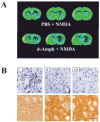
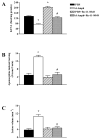
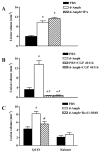
The N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) subtype of glutamate receptors plays an important role in brain physiology, but excessive receptor stimulation results in seizures and excitotoxic nerve cell death. NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal excitation and injury can be prevented by high, non-physiological concentrations of the neuroinhibitory tryptophan metabolite kynurenic acid (KYNA). Here we report that endogenous KYNA, which is formed in and released from astrocytes, controls NMDA receptors in vivo. This was revealed with the aid of the dopaminergic drugs d-amphetamine and apomorphine, which cause rapid, transient decreases in striatal KYNA levels in rats. Intrastriatal injections of the excitotoxins NMDA or quinolinate (but not the non-NMDA receptor agonist kainate) at the time of maximal KYNA reduction resulted in two- to threefold increases in excitotoxic lesion size. Pre-treatment with a kynurenine 3-hydroxylase inhibitor or with dopamine receptor antagonists, i.e., two classes of pharmacological agents that prevented the reduction in brain KYNA caused by dopaminergic stimulation, abolished the potentiation of neurotoxicity. Thus, the present study identifies a previously unappreciated role of KYNA as a functional link between dopamine receptor stimulation and NMDA neurotoxicity in the striatum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kynurenic acid leads, dopamine follows: a new case of volume transmission in the brain?J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007 Jan;114(1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s00702-006-0562-y. Epub 2006 Aug 24. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007. PMID: 16932989
-
Protection against quinolinic acid-mediated excitotoxicity in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by endogenous kynurenic acid.Neuroscience. 1997 Jun;78(4):967-75. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00655-0. Neuroscience. 1997. PMID: 9174065
-
Effect of systemic L-DOPA administration on extracellular kynurenate levels in the rat striatum.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2002 Mar;109(3):239-49. doi: 10.1007/s007020200020. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2002. PMID: 11956948
-
Endogenous kynurenate controls the vulnerability of striatal neurons to quinolinate: Implications for Huntington's disease.Exp Neurol. 2006 Jan;197(1):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Aug 15. Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16099455
-
Specific inhibition of kynurenate synthesis enhances extracellular dopamine levels in the rodent striatum.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 3;159(1):196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.11.055. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19138730 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The potential role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 for major depressive disorder.Psychiatry Investig. 2014 Jul;11(3):217-22. doi: 10.4306/pi.2014.11.3.217. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Psychiatry Investig. 2014. PMID: 25110491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The complex role of the chemokine CX3CL1/Fractalkine in major depressive disorder: A narrative review of preclinical and clinical studies.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Apr 28;38:100778. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100778. eCollection 2024 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 38706575 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Secrets: Exploring the Biochemical Correlates of Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adults with Autism Spectrum Conditions.Biomedicines. 2023 May 31;11(6):1600. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061600. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371695 Free PMC article.
-
Fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1) deficiency sensitizes mice to the behavioral changes induced by lipopolysaccharide.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Dec 17;7:93. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-93. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 21167054 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term disruption of tissue levels of glutamate and glutamatergic neurotransmission neuromodulators, taurine and kynurenic acid induced by amphetamine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Jul;241(7):1387-1398. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06570-4. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38480557
References
-
- Anderson PH. Comparison of the pharmacological characteristics of [3H]raclopride and [3H]SCH 23390 binding to dopamine receptors in vivo in mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988;146:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Becquet D, Faudon M, Hery F. In vivo evidence for an inhibitory glutamatergic control of serotonin release in the cat caudate nucleus: involvement of GABA neurons. Brain Res. 1990;519:82–88. - PubMed
-
- Bernard V, Bolam JP. Subcellular and subsynaptic distribution of the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor in the neostriatum and globus pallidus of the rat: co-localization at synapses with the GluR2/3 subunit of the AMPA receptor. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:3721–3736. - PubMed
-
- Buisson A, Pateau V, Plotkine M, Boulu RG. Nigrostriatal pathway modulates striatum vulnerability to quinolinic acid. Neurosci Lett. 1991;131:257–259. - PubMed
-
- Carpenedo R, Pittaluga A, Cozzi A, Attucci S, Galli A, Raiteri M, Moroni F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13:2141–2147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

