Fungal CSL transcription factors
- PMID: 17629904
- PMCID: PMC1973085
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-233
Fungal CSL transcription factors
Abstract
Background: The CSL (CBF1/RBP-Jkappa/Suppressor of Hairless/LAG-1) transcription factor family members are well-known components of the transmembrane receptor Notch signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in metazoan development. They function as context-dependent activators or repressors of transcription of their responsive genes, the promoters of which harbor the GTG(G/A)GAA consensus elements. Recently, several studies described Notch-independent activities of the CSL proteins.
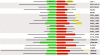
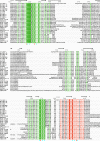
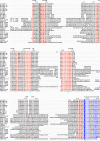
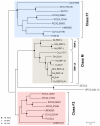
Results: We have identified putative CSL genes in several fungal species, showing that this family is not confined to metazoans. We have analyzed their sequence conservation and identified the presence of well-defined domains typical of genuine CSL proteins. Furthermore, we have shown that the candidate fungal protein sequences contain highly conserved regions known to be required for sequence-specific DNA binding in their metazoan counterparts. The phylogenetic analysis of the newly identified fungal CSL proteins revealed the existence of two distinct classes, both of which are present in all the species studied.
Conclusion: Our findings support the evolutionary origin of the CSL transcription factor family in the last common ancestor of fungi and metazoans. We hypothesize that the ancestral CSL function involved DNA binding and Notch-independent regulation of transcription and that this function may still be shared, to a certain degree, by the present CSL family members from both fungi and metazoans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fission yeast CSL proteins function as transcription factors.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059435. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555033 Free PMC article.
-
N-termini of fungal CSL transcription factors are disordered, enriched in regulatory motifs and inhibit DNA binding in fission yeast.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023650. Epub 2011 Aug 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21858190 Free PMC article.
-
Cbf11 and Cbf12, the fission yeast CSL proteins, play opposing roles in cell adhesion and coordination of cell and nuclear division.Exp Cell Res. 2009 May 1;315(8):1533-47. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.12.001. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19101542
-
Nutrient sensing-the key to fungal p53-like transcription factors?Fungal Genet Biol. 2019 Mar;124:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Fungal Genet Biol. 2019. PMID: 30579885 Review.
-
The effects of conformational heterogeneity on the binding of the Notch intracellular domain to effector proteins: a case of biologically tuned disorder.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Apr;36(Pt 2):157-66. doi: 10.1042/BST0360157. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18363556 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitotic defects in fission yeast lipid metabolism 'cut' mutants are suppressed by ammonium chloride.FEMS Yeast Res. 2018 Sep 1;18(6):foy064. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foy064. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018. PMID: 29931271 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and evolution of the Notch signalling pathway: an overview from eukaryotic genomes.BMC Evol Biol. 2009 Oct 13;9:249. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-249. BMC Evol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19825158 Free PMC article.
-
Cbf11 and Mga2 function together to activate transcription of lipid metabolism genes and promote mitotic fidelity in fission yeast.PLoS Genet. 2024 Dec 9;20(12):e1011509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011509. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39652606 Free PMC article.
-
Fission Yeast CSL Transcription Factors: Mapping Their Target Genes and Biological Roles.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137820. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26366556 Free PMC article.
-
Fission yeast CSL proteins function as transcription factors.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059435. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555033 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

