Distribution and characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from surface waters of the South Nation River watershed, Ontario, Canada
- PMID: 17630309
- PMCID: PMC2042075
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00354-07
Distribution and characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from surface waters of the South Nation River watershed, Ontario, Canada
Abstract
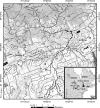
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen thought to be widely distributed in the environment. We investigated the prevalence and characteristics of L. monocytogenes isolates from surface waters derived from catchments within the South Nation River watershed (Ontario, Canada). This watershed is dominated by urban and rural development, livestock and crop production, and wildlife habitats. From June to November 2005, a total of 314 surface water samples were collected biweekly from 22 discrete sampling sites characterized by various upstream land uses. Presumptive Listeria spp. were isolated using a selective enrichment and isolation procedure, and 75 L. monocytogenes isolates were identified based on colony morphology, hemolytic activity, and amplification of three pathogenicity genes: iap, inlA, and hlyA. Thirty-two of 314 (10%) surface water samples were positive for the presence of L. monocytogenes, but detection ranged between 0 and 27% depending on the sampling date. Isolates belonging to serovar group 1/2a, 3a (50%) and group 4b, 4d, 4e (32%) were dominant. L. monocytogenes populations were resolved into 13 EcoRI ribotypes and 21 ApaI and 21 AscI pulsotypes. These had Simpson indexes of discrimination of up to 0.885. Lineage I-related isolates were dominant (61%) during the summer, whereas lineage II isolates were dominant (77%) in the fall. Isolates were, on average, resistant to 6.1 +/- 2.1 antibiotics out of 17 tested. Half of the L. monocytogenes isolates exhibited potential virulence linked to the production of a functional internalin A, and some isolates were found to be moderately to highly virulent by in vitro Caco-2 plaque formation assay (up to 28% of entry). There was a statistically significant link between the occurrence of L. monocytogenes and proximity to an upstream dairy farm and degree of cropped land. Our data indicate that L. monocytogenes is widespread in the studied catchments, where it could represent a public health issue related to agricultural land use.
Figures


References
-
- Arvanitidou, M., A. Papa, T. C. Constantinidis, V. Danielides, and V. Katsouyannopoulos. 1997. The occurrence of Listeria spp. and Salmonella spp. in surface waters. Microbiol. Res. 152:395-397. - PubMed
-
- Aureli, P., A. M. Ferrini, V. Mannoni, S. Hodzic, C. Wedell-Weergaard, and B. Oliva. 2003. Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from food in Italy to antibiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 83:325-330. - PubMed
-
- Ball Coelho, B. R., R. C. Roy, E. Topp, and D. R. Lapen. 2007. Tile water quality following liquid swine manure application into standing corn. J. Environ. Qual. 36:580-587. - PubMed
-
- Brackett, R. E. 1999. Incidence, contributing factors, and control of bacterial pathogens in produce. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 15:305-311.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

