Elongation factor G stabilizes the hybrid-state conformation of the 70S ribosome
- PMID: 17630323
- PMCID: PMC1950763
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.601507
Elongation factor G stabilizes the hybrid-state conformation of the 70S ribosome
Abstract
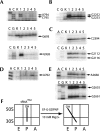
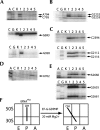
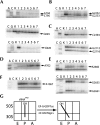
Following peptide bond formation, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and messenger RNA (mRNA) are translocated through the ribosome, a process catalyzed by elongation factor EF-G. Here, we have used a combination of chemical footprinting, peptidyl transferase activity assays, and mRNA toeprinting to monitor the effects of EF-G on the positions of tRNA and mRNA relative to the A, P, and E sites of the ribosome in the presence of GTP, GDP, GDPNP, and fusidic acid. Chemical footprinting experiments show that binding of EF-G in the presence of the non-hydrolyzable GTP analog GDPNP or GDP.fusidic acid induces movement of a deacylated tRNA from the classical P/P state to the hybrid P/E state. Furthermore, stabilization of the hybrid P/E state by EF-G compromises P-site codon-anticodon interaction, causing frame-shifting. A deacylated tRNA bound to the P site and a peptidyl-tRNA in the A site are completely translocated to the E and P sites, respectively, in the presence of EF-G with GTP or GDPNP but not with EF-G.GDP. Unexpectedly, translocation with EF-G.GTP leads to dissociation of deacylated tRNA from the E site, while tRNA remains bound in the presence of EF-G.GDPNP, suggesting that dissociation of tRNA from the E site is promoted by GTP hydrolysis and/or EF-G release. Our results show that binding of EF-G in the presence of GDPNP or GDP.fusidic acid stabilizes the ribosomal intermediate hybrid state, but that complete translocation is supported only by EF-G.GTP or EF-G.GDPNP.
Figures




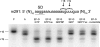
References
-
- Abel, K., Jurnak, F. A complex profile of protein elongation: Translating chemical energy into molecular movement. Structure. 1996;4:229–238. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal, R.K., Penczek, P., Grassucci, R.A., Burkhardt, N., Nierhaus, K.H., Frank, J. Effect of buffer conditions on the position of tRNA on the 70 S ribosome as visualized by cryoelectron microscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:8723–8729. - PubMed
-
- Belitsina, N.V., Glukhova, M.A., Spirin, A.S. Translocation in ribosomes by attachment–detachment of elongation factor G without GTP cleavage: Evidence from a column-bound ribosome system. FEBS Lett. 1975;54:35–38. - PubMed
-
- Belitsina, N.V., Glukhova, M.A., Spirin, A.S. Elongation factor G-promoted translocation and polypeptide elongation in ribosomes without GTP cleavage: Use of columns with matrix-bound polyuridylic acid. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:761–779. - PubMed
-
- Bodley, J.W., Zieve, F.J., Lin, L. Studies on translocation. IV. The hydrolysis of a single round of guanosine triphosphate in the presence of fusidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1970;245:5662–5667. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
