Dietary fat intake and relationship to serum lipid levels in HIV-infected patients with metabolic abnormalities in the HAART era
- PMID: 17630554
- PMCID: PMC4393713
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32823644ff
Dietary fat intake and relationship to serum lipid levels in HIV-infected patients with metabolic abnormalities in the HAART era
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate dietary intake and its relationship to lipid parameters in HIV-infected patients with metabolic abnormalities.
Method: We prospectively determined dietary intake (4-day food records or 24-h recall) in 356 HIV-infected patients and 162 community-derived HIV-negative controls evaluated for metabolic studies between 1998-2005. Differences in dietary intake between HIV-infected patients and non-HIV-infected controls, in relation to the established 2005 USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) Recommended Dietary Guidelines, were determined. The relationship between dietary fat intake and serum lipid levels among HIV-infected individuals was also evaluated.
Results: Assessment of dietary intake in this group of HIV-infected patients demonstrated increased intake of total dietary fat (P < 0.05), saturated fat (P = 0.006), and cholesterol (P = 0.006) as well as a greater percentage of calories from saturated fat (P = 0.002) and from trans fat (P = 0.02), despite similar caloric intake to the control individuals. A significantly higher percentage of HIV-infected patients were above the 2005 USDA Recommended Dietary Guidelines for saturated fat (> 10%/day) (76.0% HIV vs. 60.9% controls, P = 0.003), and cholesterol (> 300 mg/day) (49.7% HIV vs. 37.9% controls, P = 0.04). Saturated fat intake was strongly associated with triglyceride level [triglyceride level increased 8.7 mg/dl (parameter estimate) per gram of increased saturated fat intake, P = 0.005] whereas total fat was inversely associated with triglyceride level [triglyceride level decreased 3.0 mg/dl (parameter estimate) per gram of increased total fat intake, P = 0.02] among HIV-infected individuals.
Conclusions: Increased intake of saturated fat is seen and contributes to hypertriglyceridemia among HIV-infected patients who have developed metabolic abnormalities. Increased saturated fat intake should be targeted for dietary modification in this population.
Figures
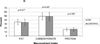
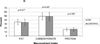
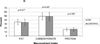
References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Carr A, Samaras K, Burton S, Law M, Freund J, Chisholm DJ, et al. A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1998;12:F51–F58. - PubMed
-
- Morse CG, Kovacs JA. Metabolic and skeletal complications of HIV infection: the price of success. JAMA. 2006;296:844–854. - PubMed
-
- Friis-Moller N, Sabin CA, Weber R, d’Arminio Monforte A, El-Sadr WM, Reiss P, et al. Combination antiretroviral therapy and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1993–2003. - PubMed
-
- Depairon M, Chessex S, Sudre P, Rodondi N, Doser N, Chave JP, et al. Premature atherosclerosis in HIV-infected individuals--focus on protease inhibitor therapy. AIDS. 2001;15:329–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

