Chemokine signaling specificity: essential role for the N-terminal domain of chemokine receptors
- PMID: 17630697
- PMCID: PMC2727729
- DOI: 10.1021/bi7004043
Chemokine signaling specificity: essential role for the N-terminal domain of chemokine receptors
Erratum in
- Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 16;46(41):11660
Abstract
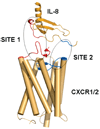
Chemokine IL-8 (CXCL8) binds to its cognate receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 to induce inflammatory responses, wound healing, tumorogenesis, and neuronal survival. Here we identify the N-loop residues in IL-8 (H18 and F21) and the receptor N-termini as the major structural determinants regulating the rate of receptor internalization, which in turn controlled the activation profile of ERK1/2, a central component of the receptor/ERK signaling pathway that dictates signal specificity. Our data further support the idea that the chemokine receptor core acts as a plastic scaffold. Thus, the diversity and intensity of inflammatory and noninflammatory responses mediated by chemokine receptors appear to be primarily determined by the initial interaction between the receptor N-terminus and the N-loop of chemokines.
Figures





References
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Onuffer JJ, Horuk R. Chemokines, chemokine receptors and small-molecule antagonists: Recent developments. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002;23:459–467. - PubMed
-
- Thelen M. Dancing to the tune of chemokines. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Baruch A, Bengali K, Tani K, Xu L, Oppenheim JJ, Wang JM. IL-8 and NAP-2 differ in their capacities to bind and chemoattract 293 cells transfected with either IL-8 receptor type A or type B. Cytokine. 1997;9:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Baruch A, Grimm M, Bengali K, Evans GA, Chertov O, Wang JM, Howard OM, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Oppenheim JJ. The differential ability of IL-8 and neutrophil-activating peptide-2 to induce attenuation of chemotaxis is mediated by their divergent capabilities to phosphorylate CXCR2 (IL-8 receptor B) J. Immunol. 1997;158:5927–5933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

