The X family portrait: structural insights into biological functions of X family polymerases
- PMID: 17631059
- PMCID: PMC2128704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.05.009
The X family portrait: structural insights into biological functions of X family polymerases
Abstract
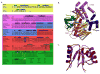
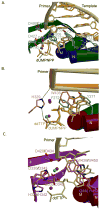
The mammalian family X DNA polymerases (DNA polymerases beta, lambda, mu, and TdT) contribute to base excision repair and double-strand break repair by virtue of their ability to fill short gaps in DNA. Structural information now exists for all four of these enzymes, making this the first mammalian polymerase family whose structural portrait is complete. Here we consider how distinctive structural features of these enzymes contribute to their biological functions in vivo.
Figures






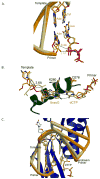
References
-
- Bebenek K, Kunkel TA. Functions of DNA Polymerases. Adv Protein Chem. 2004;69:137–165. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto Y, Kim K. Excision of deoxyribose phosphate residues by DNA polymerase beta during DNA repair. Science. 1995;269:699–702. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Diaz M, Bebenek K, Kunkel TA, Blanco L. Identification of an intrinsic 5′-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity in human DNA polymerase lambda: a possible role in base excision repair. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:34659–34663. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava DK, Berg BJ, Prasad R, Molina JT, Beard WA, Tomkinson AE, Wilson SH. Mammalian abasic site base excision repair. Identification of the reaction sequence and rate-determining steps. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:21203–21209. - PubMed
-
- Braithwaite EK, Prasad R, Shock DD, Hou EW, Beard WA, Wilson SH. DNA polymerase lambda mediates a back-up base excision repair activity in extracts of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18469–18475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

