Referral patterns, cancer diagnoses, and waiting times after introduction of two week wait rule for breast cancer: prospective cohort study
- PMID: 17631514
- PMCID: PMC1941875
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39258.688553.55
Referral patterns, cancer diagnoses, and waiting times after introduction of two week wait rule for breast cancer: prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the long term impact of the two week wait rule for breast cancer on referral patterns, cancer diagnoses, and waiting times.
Design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting: A specialist breast clinic in a teaching hospital in Bristol.
Participants: All patients referred to breast clinic from primary care between 1999 and 2005.
Main outcome measures: Number, route, and outcome of referrals from primary care and waiting times for urgent and routine appointments.
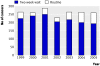
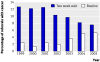
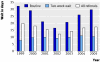
Results: The annual number of referrals increased by 9% over the seven years from 3499 in 1999 to 3821 in 2005. Routine referrals decreased by 24% (from 1748 to 1331), but two week wait referrals increased by 42% (from 1751 to 2490) during this time. The percentage of patients diagnosed with cancer in the two week wait group decreased from 12.8% (224/1751) in 1999 to 7.7% (191/2490) in 2005 (P<0.001), while the number of cancers detected in the "routine" group increased from 2.5% (43/1748) to 5.3% (70/1331) (P<0.001) over the same period. About 27% (70/261) of people with cancer are currently referred in the non-urgent group. Waiting times for routine referrals have increased with time.
Conclusion: The two week wait rule for breast cancer is failing patients. The number of cancers detected in the two week wait population is decreasing, and an unacceptable proportion is now being referred via the routine route. If breast cancer services are to be improved, the two week wait rule should be reviewed urgently.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Two week rule: Breast cancer growth rates favour abolition of rule.BMJ. 2007 Aug 25;335(7616):361. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39311.468183.3A. BMJ. 2007. PMID: 17717340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Two week rule: Breast cancer experience has wider implications.BMJ. 2007 Aug 25;335(7616):361. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39311.512396.3A. BMJ. 2007. PMID: 17717341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bray F, Sankila R, Ferlay J, Parkin DM. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe. Eur J Cancer 2002;38:99-166. - PubMed
-
- Health Service Circular HCS 1998/242. Breast cancer waiting times—achieving the two week target 1998. www.dh.gov.uk/PublicationsAndStatistics/LettersAndCirculars/HealthServic...
-
- Fentiman IS. Two week wait for suspected cancer: milestone or millstone? Int J Clin Pract 2005;59:1247-52. - PubMed
-
- Cant PJ, Yu DSL. Impact of the “2 week wait” directive for suspected cancer on service provision in a symptomatic breast clinic. Br J Surg 2000;87:1082-6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
