The Arabidopsis BAP1 and BAP2 genes are general inhibitors of programmed cell death
- PMID: 17631528
- PMCID: PMC1976577
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.100800
The Arabidopsis BAP1 and BAP2 genes are general inhibitors of programmed cell death
Abstract
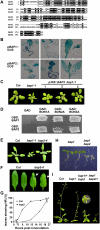
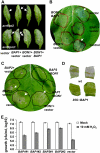
Here we identify the BAP1 and BAP2 genes of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) as general inhibitors of programmed cell death (PCD) across the kingdoms. These two homologous genes encode small proteins containing a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding C2 domain. BAP1 and its functional partner BON1 have been shown to negatively regulate defense responses and a disease resistance gene SNC1. Genetic studies here reveal an overlapping function of the BAP1 and BAP2 genes in cell death control. The loss of BAP2 function induces accelerated hypersensitive responses but does not compromise plant growth or confer enhanced resistance to virulent bacterial or oomycete pathogens. The loss of both BAP1 and BAP2 confers seedling lethality mediated by PAD4 and EDS1, two regulators of cell death and defense responses. Overexpression of BAP1 or BAP2 with their partner BON1 inhibits PCD induced by pathogens, the proapoptotic gene BAX, and superoxide-generating paraquat in Arabidopsis or Nicotiana benthamiana. Moreover, expressing BAP1 or BAP2 in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) alleviates cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. Thus, the BAP genes function as general negative regulators of PCD induced by biotic and abiotic stimuli including reactive oxygen species. The dual roles of BAP and BON genes in repressing defense responses mediated by disease resistance genes and in inhibiting general PCD has implications in understanding the evolution of plant innate immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Adam L, Somerville SC (1996) Genetic characterization of five powdery mildew disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 9 341–356 - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ, Staskawicz BJ (2003) Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112 369–377 - PubMed
-
- Azevedo C, Sadanandom A, Kitagawa K, Freialdenhoven A, Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P (2002) The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science 295 2073–2076 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

