Influence of water clustering on the dynamics of hydration water at the surface of a lysozyme
- PMID: 17631539
- PMCID: PMC2025659
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.108753
Influence of water clustering on the dynamics of hydration water at the surface of a lysozyme
Abstract
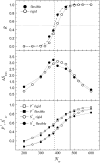
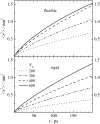
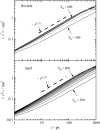
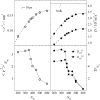
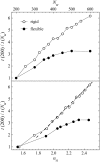
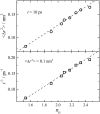
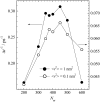
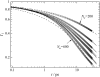
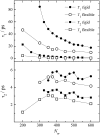
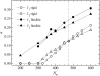
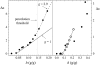
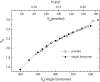
Dynamics of hydration water at the surface of a lysozyme molecule is studied by computer simulations at various hydration levels in relation with water clustering and percolation transition. Increase of the translational mobility of water molecules at the surface of a rigid lysozyme molecule upon hydration is governed by the water-water interactions. Lysozyme dynamics strongly affect translational motions of water and this dynamic coupling is maximal at hydration levels, corresponding to the formation of a spanning water network. Anomalous diffusion of hydration water does not depend on hydration level up to monolayer coverage and reflects spatial disorder. Rotational dynamics of water molecules show stretched exponential decay at low hydrations. With increasing hydration, we observe appearance of weakly bound water molecules with bulklike rotational dynamics, whose fraction achieves 20-25% at the percolation threshold.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Water in hydrated orthorhombic lysozyme crystal: Insight from atomistic simulations.J Chem Phys. 2008 Aug 21;129(7):075105. doi: 10.1063/1.2969811. J Chem Phys. 2008. PMID: 19044806
-
Water rotational relaxation and diffusion in hydrated lysozyme.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Jun 12;124(23):6787-91. doi: 10.1021/ja025905m. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12047201
-
Formation of spanning water networks on protein surfaces via 2D percolation transition.J Phys Chem B. 2005 Feb 10;109(5):1988-98. doi: 10.1021/jp045903j. J Phys Chem B. 2005. PMID: 16851183
-
Observation of high-temperature dynamic crossover in protein hydration water and its relation to reversible denaturation of lysozyme.J Chem Phys. 2009 Apr 7;130(13):135101. doi: 10.1063/1.3081137. J Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19355784
-
Dynamics of hydration in hen egg white lysozyme.J Mol Biol. 2001 Aug 10;311(2):409-19. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4860. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11478869
Cited by
-
Profiling of dynamics in protein-lipid-water systems: a time-resolved fluorescence study of a model membrane protein with the label BADAN at specific membrane depths.Eur Biophys J. 2010 Mar;39(4):647-56. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0538-6. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Eur Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 19760185 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosecond motions in proteins impose bounds on the timescale distributions of local dynamics.Biophys J. 2009 Oct 7;97(7):2080-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.07.036. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19804740 Free PMC article.
-
NMR evidence of a sharp change in a measure of local order in deeply supercooled confined water.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 2;105(35):12725-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805032105. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18753633 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed study of the dielectric function of a lysozyme solution studied with molecular dynamics simulations.Eur Biophys J. 2015 Dec;44(8):599-611. doi: 10.1007/s00249-015-1052-7. Epub 2015 Jun 21. Eur Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26094070
-
Nonthermal acceleration of protein hydration by sub-terahertz irradiation.Nat Commun. 2023 May 22;14(1):2825. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38462-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37217486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaplin, M. 2006. Do we underestimate the importance of water in cell biology? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:861–866. - PubMed
-
- Levy, Y., and J. N. Onuchic. 2006. Water mediation in protein folding and molecular recognition. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 35:389–415. - PubMed
-
- Helms, V. 2007. Protein dynamics tightly connected to the dynamics of surrounding and internal water molecules. Chem. Phys. Chem. 8:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Clegg, J. S. 1974. Interrelationships between water and metabolism in Artemia salina cysts: hydration-dehydration from the liquid and vapor phases. J. Exp. Biol. 61:291–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

