A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells
- PMID: 17632057
- PMCID: PMC3200295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.042
A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells
Abstract
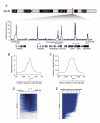
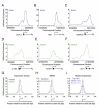
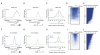
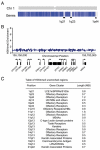
We describe the results of a genome-wide analysis of human cells that suggests that most protein-coding genes, including most genes thought to be transcriptionally inactive, experience transcription initiation. We found that nucleosomes with H3K4me3 and H3K9,14Ac modifications, together with RNA polymerase II, occupy the promoters of most protein-coding genes in human embryonic stem cells. Only a subset of these genes produce detectable full-length transcripts and are occupied by nucleosomes with H3K36me3 modifications, a hallmark of elongation. The other genes experience transcription initiation but show no evidence of elongation, suggesting that they are predominantly regulated at postinitiation steps. Genes encoding most developmental regulators fall into this group. Our results also identify a class of genes that are excluded from experiencing transcription initiation, at which mechanisms that prevent initiation must predominate. These observations extend to differentiated cells, suggesting that transcription initiation at most genes is a general phenomenon in human cells.
Figures


Comment in
-
RNA polymerase II: just stopping by.Cell. 2007 Jul 13;130(1):16-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.040. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17632051
References
-
- Abeyta MJ, Clark AT, Rodriguez RT, Bodnar MS, Pera RA, Firpo MT. Unique gene expression signatures of independently-derived human embryonic stem cell lines. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:601–608. - PubMed
-
- Agalioti T, Chen G, Thanos D. Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell. 2002;111:381–392. - PubMed
-
- Azuara V, Perry P, Sauer S, Spivakov M, Jorgensen HF, John RM, Gouti M, Casanova M, Warnes G, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG. Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Schneider R, Myers FA, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C, Kouzarides T. Spatial distribution of di- and trimethyl lysine 36 of histone H3 at active genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:17732–17736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

