Structural constraints on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef function
- PMID: 17632197
- PMCID: PMC3026346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.02.036
Structural constraints on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef function
Abstract
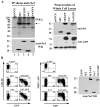
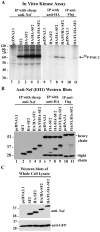
HIV-1 Nef is a multifunctional protein that exerts its activities through interactions with multiple cellular partners. Nef uses different domains and mechanisms to exert its functions including cell surface down-modulation of CD4 and MHC-I receptors and activation of the serine/threonine kinase PAK-2. We inserted tags at the C-terminus and proximal to the N-terminus of Nef and the effects on Nef's structure/function relationships were examined. We discovered significant defects in MHC-I down-modulation with the insertion of HA/FLAG tags at either region. We also found impaired PAK-2 activation with a C-terminal fusion with GFP. Interestingly, Nef-GFP and Nef-GH(7) induced MHC-I down-modulation, suggesting that the negative charge of the HA/FLAG tag could contribute to the observed defect. Together, these observations highlight elements of Nef's functional complexity and demonstrate previously unsuspected structural requirements for PAK-2 activation and MHC-1 down-modulation in Nef's flexible N- and C-terminal regions.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nef-induced CD4 and major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) down-regulation are governed by distinct determinants: N-terminal alpha helix and proline repeat of Nef selectively regulate MHC-I trafficking.J Virol. 1999 Mar;73(3):1964-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.3.1964-1973.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9971776 Free PMC article.
-
Simian and human immunodeficiency virus Nef proteins use different surfaces to downregulate class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(12):5691-701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.12.5691-5701.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10823877 Free PMC article.
-
Internalization and intracellular retention of CD4 are two separate functions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein.J Gen Virol. 2007 Nov;88(Pt 11):3133-3138. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.83164-0. J Gen Virol. 2007. PMID: 17947540
-
HIV-1 Nef: a master manipulator of the membrane trafficking machinery mediating immune evasion.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1850(4):733-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25585010 Review.
-
The downregulation of CD4 and MHC-I by primate lentiviruses: a paradigm for the modulation of cell surface receptors.Immunol Rev. 1999 Apr;168:51-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01282.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10399064 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-association of the Lentivirus protein, Nef.Retrovirology. 2010 Sep 23;7:77. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-77. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20863404 Free PMC article.
-
Neutron reflectometry study of the conformation of HIV Nef bound to lipid membranes.Biophys J. 2010 Sep 22;99(6):1940-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.07.016. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20858440 Free PMC article.
-
Subverting Host Cell P21-Activated Kinase: A Case of Convergent Evolution across Pathogens.Pathogens. 2017 Apr 21;6(2):17. doi: 10.3390/pathogens6020017. Pathogens. 2017. PMID: 28430160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational transition of membrane-associated terminally acylated HIV-1 Nef.Structure. 2013 Oct 8;21(10):1822-33. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Structure. 2013. PMID: 24035710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arold S, Franken P, Strub MP, Hoh F, Benichou S, Benarous R, Dumas C. The crystal structure of HIV-1 Nef protein bound to the Fyn kinase SH3 domain suggests a role for this complex in altered T cell receptor signaling. Structure. 1997;5(10):1361–72. - PubMed
-
- Arold ST, Baur AS. Dynamic Nef and Nef dynamics: how structure could explain the complex activities of this small HIV protein. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26(6):356–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

