The positions of TFIIF and TFIIE in the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex
- PMID: 17632521
- PMCID: PMC2483787
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1272
The positions of TFIIF and TFIIE in the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex
Abstract
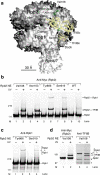
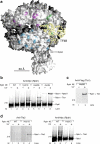
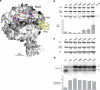
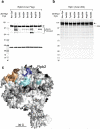
We incorporated the non-natural photoreactive amino acid p-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine (Bpa) into the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) surface surrounding the central cleft formed by the Rpb1 and Rpb2 subunits. Photo-cross-linking of preinitiation complexes (PICs) with these Pol II derivatives and hydroxyl-radical cleavage assays revealed that the TFIIF dimerization domain interacts with the Rpb2 lobe and protrusion domains adjacent to Rpb9, while TFIIE cross-links to the Rpb1 clamp domain on the opposite side of the Pol II central cleft. Mutations in the Rpb2 lobe and protrusion domains alter both Pol II-TFIIF binding and the transcription start site, a phenotype associated with mutations in TFIIF, Rpb9 and TFIIB. Together with previous biochemical and structural studies, these findings illuminate the structural organization of the PIC and the network of protein-protein interactions involved in transcription start site selection.
Figures



Comment in
-
Finding the right spot to start transcription.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Aug;14(8):686-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0807-686. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17676030 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Position of the general transcription factor TFIIF within the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex.EMBO J. 2010 Feb 17;29(4):706-16. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.386. Epub 2009 Dec 24. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20033062 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-TFIIF complex revealed by cross-linking and mass spectrometry.EMBO J. 2010 Feb 17;29(4):717-26. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.401. Epub 2010 Jan 21. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20094031 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the location of TFIIB within the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex: a model for the structure of the PIC.Cell. 2004 Oct 15;119(2):169-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.028. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15479635
-
Conservation between the RNA polymerase I, II, and III transcription initiation machineries.Mol Cell. 2012 Feb 24;45(4):439-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.023. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22365827 Review.
-
RNA polymerase II elongation factors use conserved regulatory mechanisms.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Feb;84:102766. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102766. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38181687 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of mammalian transcription by Gdown1 through a novel steric crosstalk revealed by cryo-EM.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 29;31(17):3575-87. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.205. Epub 2012 Jul 31. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22850672 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that RNA polymerase II and not TFIIB is responsible for the difference in transcription initiation patterns between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Aug;40(14):6495-507. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks323. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22510268 Free PMC article.
-
Photocrosslinking approaches to interactome mapping.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Feb;17(1):90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.034. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23149092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The initiation factor TFE and the elongation factor Spt4/5 compete for the RNAP clamp during transcription initiation and elongation.Mol Cell. 2011 Jul 22;43(2):263-74. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.05.030. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21777815 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping RNA exit channel on transcribing RNA polymerase II by FRET analysis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 6;106(1):127-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811689106. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19109435 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

