The distribution of sexually-transmitted Human Papillomaviruses in HIV positive and negative patients in Zambia, Africa
- PMID: 17634108
- PMCID: PMC1949816
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-7-77
The distribution of sexually-transmitted Human Papillomaviruses in HIV positive and negative patients in Zambia, Africa
Abstract
Background: Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) are double-stranded DNA viruses, considered to be the primary etiological agents in cervical intraepithelial neoplasias and cancers. Approximately 15-20 of the 40 mucosal HPVs confer a high-risk of progression of lesions to invasive cancer. In this study, we investigated the prevalence of sexually transmitted HPVs in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) positive and negative patients in Zambia, Africa. The rate of high-risk HPV genotypes worldwide varies within each country. Thus, we sought to investigate the rates of HPV infection in sub-Saharan Africa and the potential role of HIV in affecting the HPV genotype distribution.
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional study reports findings on the association and effects of HIV on HPV infections in an existing cohort of patients at University Teaching Hospital (UTH) Lusaka, Zambia. The objective of this study was to assess HPV prevalence, genotype distribution and to identify co-factors that influence HPV infection. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with two standard consensus primer sets (CpI/II and GP5+/6+) was used to test for the presence of HPV DNA. Primers specific for beta-actin were used to monitor DNA quality. Vaginal lavage samples, collected between 1998-1999 from a total of 70 women, were part of a larger cohort that was also analyzed for HIV and human herpesvirus infection. Seventy of the samples yielded usable DNA. HIV status was determined by two rapid assays, Capillus and Determine. The incidence of HIV and HPV infections and HPV genotype distributions were calculated and statistical significance was determined by Chi-Squared test.
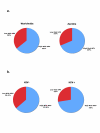
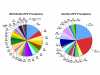
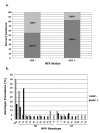
Results: We determined that most common HPV genotypes detected among these Zambian patients were types 16 and 18 (21.6% each), which is approximately three-fold greater than the rates for HPV16, and ten-fold greater than the rates for HPV18 in the United States. The worldwide prevalence of HPV16 is approximately 14% and HPV18 is 5%. The overall ratio of high-risk (HR) to low-risk (LR) HPVs in the patient cohort was 69% and 31% respectively; essentially identical to that for the HR and LR distributions worldwide. However, we discovered that HIV positive patients were two-times as likely to have an HR HPV as HIV negative individuals, while the distribution of LR HPVs was unaffected by HIV status. Interestingly, we observed a nine-fold increase in HPV18 infection frequency in HIV positive versus HIV negative individuals.
Conclusion: The rate of oncogenic HPVs (type 16 and 18) in Zambia was much higher than in the U.S., potentially providing an explanation for the high-rates of cervical cancer in Zambia. Surprisingly, we discovered a strong association between positive HIV status and the prevalence of HR HPVs, and specifically HPV18.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and type distribution of human papillomavirus among 1813 men in Tanzania and the relationship to HIV status.Sex Transm Dis. 2013 Jul;40(7):592-8. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31828fcf57. Sex Transm Dis. 2013. PMID: 23965778
-
High Concordance between Vaginal Samples and Cervical Samples of Human Papillomavirus in Women Living with HIV in Rwanda.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 15;25(1):527. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10840-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40234747 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus genotypes in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients with anal pathology in Madrid, Spain.Diagn Pathol. 2013 Dec 10;8:204. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-204. Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24325764 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus infection and associated disease in persons infected with human immunodeficiency virus.Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Aug;21 Suppl 1:S121-4. doi: 10.1093/clinids/21.supplement_1.s121. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. PMID: 8547501 Review.
-
Biology and pathological associations of the human papillomaviruses: a review.Malays J Pathol. 1998 Jun;20(1):1-10. Malays J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10879257 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of HIV infection on metastatic cervical cancer and age at diagnosis among patients in Lusaka, Zambia.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022 Mar;156(3):521-528. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13784. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 34121186 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes and preventive practices for human Papilloma virus infection among female sex workers in Lagos metropolis.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Aug 14;36:278. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.278.17912. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 33088407 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the Cervical Microbiome, HIV Status, and Precancerous Lesions.mBio. 2019 Feb 19;10(1):e02785-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02785-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30782659 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple HPV infections in female sex workers in Western Kenya: implications for prophylactic vaccines within this sub population.Infect Agent Cancer. 2017 Jan 6;12:2. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0114-5. eCollection 2017. Infect Agent Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28070215 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical cancer risk and impact of Pap-based screening in HIV-positive women on antiretroviral therapy in Johannesburg, South Africa.Int J Cancer. 2017 Aug 1;141(3):488-496. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30749. Epub 2017 May 19. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28440019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schiffman M, Castle PE. Human papillomavirus: epidemiology and public health. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127:930–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

